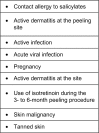
Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 26347269
- PMCID: PMC4554394
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S84765
Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review
Abstract
Salicylic acid has been used to treat various skin disorders for more than 2,000 years. The ability of salicylic acid to exfoliate the stratum corneum makes it a good agent for peeling. In particular, the comedolytic property of salicylic acid makes it a useful peeling agent for patients with acne. Once considered as a keratolytic agent, the role of salicylic acid as a desmolytic agent, because of its ability to disrupt cellular junctions rather than breaking or lysing intercellular keratin filaments, is now recognized and is discussed here. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent has a number of indications, including acne vulgaris, melasma, photodamage, freckles, and lentigines. The efficacy and safety of salicylic acid peeling in Fitzpatrick skin types I-III as well as in skin types V and VI have been well documented in the literature. This paper reviews the available data and literature on salicylic acid as a peeling agent and its possible indications. Its properties, efficacy and safety, the peeling procedure, and possible side effects are discussed in detail. An account of salicylism is also included.
Keywords: acne vulgaris; desmolytic agent; melasma; photodamage; salicylic acid.
Figures
References
-
- Khunger N. Standard guidelines of care for chemical peels. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:S5–S12. - PubMed
-
- Lin AN, Nakatsui T. Salicylic acid revisited. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:335–342. - PubMed
-
- Draelos ZD. Rediscovering the cutaneous benefits of salicylic acid. Cosm Derm. 1997;10(Suppl 4):4.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical