A novel IL-17 signaling pathway controlling keratinocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis via the TRAF4-ERK5 axis
- PMID: 26347473
- PMCID: PMC4577838
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20150204
A novel IL-17 signaling pathway controlling keratinocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis via the TRAF4-ERK5 axis
Abstract
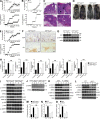
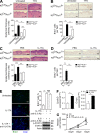
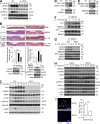
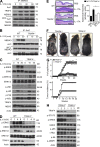
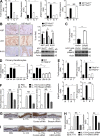
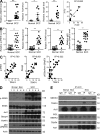
Although IL-17 is emerging as an important cytokine in cancer promotion and progression, the underlining molecular mechanism remains unclear. Previous studies suggest that IL-17 (IL-17A) sustains a chronic inflammatory microenvironment that favors tumor formation. Here we report a novel IL-17-mediated cascade via the IL-17R-Act1-TRAF4-MEKK3-ERK5 positive circuit that directly stimulates keratinocyte proliferation and tumor formation. Although this axis dictates the expression of target genes Steap4 (a metalloreductase for cell metabolism and proliferation) and p63 (a transcription factor for epidermal stem cell proliferation), Steap4 is required for the IL-17-induced sustained expansion of p63(+) basal cells in the epidermis. P63 (a positive transcription factor for the Traf4 promoter) induces TRAF4 expression in keratinocytes. Thus, IL-17-induced Steap4-p63 expression forms a positive feedback loop through p63-mediated TRAF4 expression, driving IL-17-dependent sustained activation of the TRAF4-ERK5 axis for keratinocyte proliferation and tumor formation.
© 2015 Wu et al.
Figures

References
-
- Bulek K., Liu C., Swaidani S., Wang L., Page R.C., Gulen M.F., Herjan T., Abbadi A., Qian W., Sun D., et al. . 2011. The inducible kinase IKKi is required for IL-17-dependent signaling associated with neutrophilia and pulmonary inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 12:844–852. 10.1038/ni.2080 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS071996/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS071996/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI089474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- SC1 GM111172/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI 89474-1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 10-0134/AICR_/Worldwide Cancer Research/United Kingdom
- T32GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL103453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA062220/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01 HL103453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA062220-16A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

