Brain Gαi 2 -subunit proteins and the prevention of salt sensitive hypertension
- PMID: 26347659
- PMCID: PMC4541027
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00233
Brain Gαi 2 -subunit proteins and the prevention of salt sensitive hypertension
Abstract
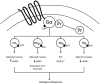
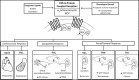
To counter the development of salt-sensitive hypertension, multiple brain G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) systems are activated to facilitate sympathoinhibition, sodium homeostasis, and normotension. Currently there is a paucity of knowledge regarding the role of down-stream GPCR-activated Gα-subunit proteins in these critically important physiological regulatory responses required for long-term blood pressure regulation. We have determined that brain Gαi2-proteins mediate natriuretic and sympathoinhibitory responses produced by acute pharmacological (exogenous central nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor (NOP) and α2-adrenoceptor activation) and physiological challenges to sodium homeostasis (intravenous volume expansion and 1 M sodium load) in conscious Sprague-Dawley rats. We have demonstrated that in salt-resistant rat phenotypes, high dietary salt intake evokes site-specific up-regulation of hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) Gαi2-proteins. Further, we established that PVN Gαi2 protein up-regulation prevents the development of renal nerve-dependent sympathetically mediated salt-sensitive hypertension in Sprague-Dawley and Dahl salt-resistant rats. Additionally, failure to up-regulate PVN Gαi2 proteins during high salt-intake contributes to the pathophysiology of Dahl salt-sensitive (DSS) hypertension. Collectively, our data demonstrate that brain, and likely PVN specific, Gαi2 protein pathways represent a central molecular pathway mediating sympathoinhibitory renal-nerve dependent responses evoked to maintain sodium homeostasis and a salt-resistant phenotype. Further, impairment of this endogenous "anti-hypertensive" mechanism contributes to the pathophysiology of salt-sensitive hypertension.
Keywords: blood pressure regulation; central G-protein coupled receptors; central Gαi2 proteins; renal sympathetic nerves; salt-sensitive hypertension; sodium homeostasis; sympathetic nervous system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Central Gαi2 Protein Mediated Neuro-Hormonal Control of Blood Pressure and Salt Sensitivity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 28;13:895466. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.895466. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35837296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gαi2-protein-mediated signal transduction: central nervous system molecular mechanism countering the development of sodium-dependent hypertension.Hypertension. 2015 Jan;65(1):178-86. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04463. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25312437 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Afferent Renal Nerve Activated Gαi2 Subunit Proteins Mediate the Natriuretic, Sympathoinhibitory and Normotensive Responses to Peripheral Sodium Challenges.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 30;12:771167. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.771167. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34916958 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Gαi2 (Guanine Nucleotide-Binding Protein Alpha Inhibiting Activity Polypeptide 2) Protein-Mediated Neural Control of the Kidney and the Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure.Hypertension. 2020 Apr;75(4):1002-1011. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13777. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32148128 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of CNS in the Effects of Salt on Blood Pressure.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016 Feb;18(2):10. doi: 10.1007/s11906-015-0620-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016. PMID: 26781250 Review.
Cited by
-
Agomelatine rescues lipopolysaccharide-induced neural injury and depression-like behaviors via suppression of the Gαi-2-PKA-ASK1 signaling pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 May 24;19(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02479-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35610704 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertensive heart disease: risk factors, complications and mechanisms.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jun 5;10:1205475. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1205475. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37342440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blunted apoptosis of erythrocytes in mice deficient in the heterotrimeric G-protein subunit Gαi2.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 8;6:30925. doi: 10.1038/srep30925. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27499046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bakris G. L., Townsend R. R., Flack J. M., Brar S., Cohen S. A., D'Agostino R., et al. . (2015). 12-month blood pressure results of catheter-based renal artery denervation for resistant hypertension: the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 65, 1314–1321. 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.01.037 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

