Vitamin D receptor and epigenetics in HIV infection and drug abuse
- PMID: 26347716
- PMCID: PMC4541325
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00788
Vitamin D receptor and epigenetics in HIV infection and drug abuse
Abstract
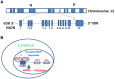
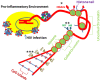
Illicit drug abuse is highly prevalent and serves as a powerful co-factor for HIV exacerbation. Epigenetic alterations in drug abuse and HIV infection determine expression of several critical genes such as vitamin D receptor (VDR), which participates in proliferation, differentiation, cell death under both physiological and pathological conditions. On that account, active vitamin D, the ligand of VDR, is used as an adjuvant therapy to control infection, slow down progression of chronic kidney diseases, and cancer chemotherapy. Interestingly, vitamin D may not be able to augment VDR expression optimally in several instances where epigenetic contributes to down regulation of VDR; however, reversal of epigenetic corruption either by demethylating agents (DACs) or histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors would be able to maximize expression of VDR in these instances.
Keywords: HIV; alcoholism; cocaine; epigenetics; gene expression regulation; opioids; vitaimin D; vitamin D receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Human Podocyte Vitamin D Receptor in HIV Milieu.J Mol Biol. 2015 Oct 9;427(20):3201-3215. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26210663 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-dependent chromatin accessibility of early vitamin D receptor target genes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1829(12):1266-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24185200
-
Vitamin-D pathway genes and HIV-1 disease progression in injection drug users.Gene. 2014 Jul 15;545(1):163-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.04.035. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24768180
-
Epigenetic corruption of VDR signalling in malignancy.Anticancer Res. 2006 Jul-Aug;26(4A):2557-66. Anticancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16886664 Review.
-
Regulation of the vitamin D receptor gene by environment, genetics and epigenetics.Gene. 2015 May 1;561(2):171-80. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.024. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25682935 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylation of the Vitamin D Receptor Gene in Human Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 20;25(1):107. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010107. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of pathogen sensitivity to antibiotics loaded in cement on the number of revisions and costs in the treatment of periprosthetic knee infection.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 Dec 21;35(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s00590-024-04166-4. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 39708185
-
Mitigating Health Risks Through Environmental Tracking of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Dec 24;82(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-04036-6. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39718600 Review.
-
Enhancement of innate immunity in gingival epithelial cells by vitamin D and HDAC inhibitors.Front Oral Health. 2024 Mar 14;5:1378566. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1378566. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38567313 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-Mediated HIV-1 Immunopathogenesis.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;15(4):628-642. doi: 10.1007/s11481-020-09960-5. Epub 2020 Oct 8. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33029670 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

