Novel Immune Check-Point Regulators in Tolerance Maintenance
- PMID: 26347744
- PMCID: PMC4539525
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00421
Novel Immune Check-Point Regulators in Tolerance Maintenance
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Novel Immune Check-Point Regulators in Tolerance Maintenance.Front Immunol. 2016 Feb 8;7:38. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00038. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26904027 Free PMC article.
Abstract
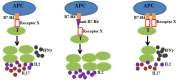
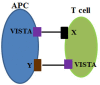
The great success of anti-cytotoxic lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA4) and anti-programed cell death protein 1 (PD1) in cancer treatment has encouraged more effort in harnessing the immune response through immunomodulatory molecules in various diseases. The immunoglobulin (Ig) super family comprises the majority of immunomodulatory molecules. Discovery of novel Ig super family members has brought novel insights into the function of different immune cells in tolerance maintenance. In this review, we discuss the function of newly identified B7 family molecules, B7-H4 and V-domain Ig Suppressor of T cell Activation (VISTA), and the butyrophilin/butyrophilin-like family members. We discuss the current stages of immunomodulatory molecules in clinical trials of organ transplantation. The potential of engaging the novel Ig superfamily members in tolerance maintenance is also discussed. We conclude with the challenges remaining to manipulate these molecules in the immune response.
Keywords: B7; butyrophilin; immune tolerance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune-checkpoint protein VISTA in allergic, autoimmune disease and transplant rejection.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 26;14:1194421. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1194421. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37435070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BTNL8, a butyrophilin-like molecule that costimulates the primary immune response.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):819-28. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.08.003. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24036152
-
B7-H4-Ig treatment of normal mice changes lymphocyte homeostasis and increases the potential of regulatory T cells.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2013 Aug;35(4):505-13. doi: 10.3109/08923973.2013.810642. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2013. PMID: 23841452
-
The B7 family revisited.Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:515-48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115611. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15771580 Review.
-
Suppression of human T-cell responses to beta-cells by activation of B7-H4 pathway.Cell Transplant. 2006;15(5):399-410. Cell Transplant. 2006. PMID: 16970282
Cited by
-
Immune-related adverse events during anticancer immunotherapy: Pathogenesis and management.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):5671-5680. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6919. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113194 Free PMC article.
-
BTNL2-Ig Protein Attenuates Type 1 Diabetes in Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mice.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 May;8(9):e1800987. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201800987. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 30884196 Free PMC article.
-
The Sweet Side of Immune Evasion: Role of Glycans in the Mechanisms of Cancer Progression.Front Oncol. 2016 Mar 9;6:54. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00054. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27014629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neonatal genetics of gene expression reveal potential origins of autoimmune and allergic disease risk.Nat Commun. 2020 Jul 28;11(1):3761. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17477-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32724101 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrophilins: an important new element of resistance.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2017;42(4):399-403. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2017.72806. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29472819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

