Discovery of Intermediary Genes between Pathways Using Sparse Regression
- PMID: 26348038
- PMCID: PMC4562633
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137222
Discovery of Intermediary Genes between Pathways Using Sparse Regression
Abstract
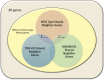
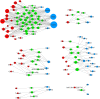
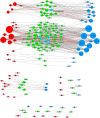
The use of pathways and gene interaction networks for the analysis of differential expression experiments has allowed us to highlight the differences in gene expression profiles between samples in a systems biology perspective. The usefulness and accuracy of pathway analysis critically depend on our understanding of how genes interact with one another. That knowledge is continuously improving due to advances in next generation sequencing technologies and in computational methods. While most approaches treat each of them as independent entities, pathways actually coordinate to perform essential functions in a cell. In this work, we propose a methodology based on a sparse regression approach to find genes that act as intermediary to and interact with two pathways. We model each gene in a pathway using a set of predictor genes, and a connection is formed between the pathway gene and a predictor gene if the sparse regression coefficient corresponding to the predictor gene is non-zero. A predictor gene is a shared neighbor gene of two pathways if it is connected to at least one gene in each pathway. We compare the sparse regression approach to Weighted Correlation Network Analysis and a correlation distance based approach using time-course RNA-Seq data for dendritic cell from wild type, MyD88-knockout, and TRIF-knockout mice, and a set of RNA-Seq data from 60 Caucasian individuals. For the sparse regression approach, we found overrepresented functions for shared neighbor genes between TLR-signaling pathway and antigen processing and presentation, apoptosis, and Jak-Stat pathways that are supported by prior research, and compares favorably to Weighted Correlation Network Analysis in cases where the gene association signals are weak.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrated analyses to reconstruct microRNA-mediated regulatory networks in mouse liver using high-throughput profiling.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S2-S12. Epub 2015 Jan 21. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25707768 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway level analysis by augmenting activities of transcription factor target genes.IET Syst Biol. 2009 Nov;3(6):534-42. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2008.0183. IET Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19947779
-
Identification of a TLR4- and TRIF-dependent activation program of dendritic cells.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Feb;34(2):558-64. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324714. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14768061
-
Gene regulatory network models: a dynamic and integrative approach to development.SEB Exp Biol Ser. 2008;61:113-39. SEB Exp Biol Ser. 2008. PMID: 18709739 Review. No abstract available.
-
Designing microarray and RNA-Seq experiments for greater systems biology discovery in modern plant genomics.Mol Plant. 2015 Feb;8(2):196-206. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.012. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25680773 Review.
Cited by
-
A Pilot Study Using a Multistaged Integrated Analysis of Gene Expression and Methylation to Evaluate Mechanisms for Evening Fatigue in Women Who Received Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer.Biol Res Nurs. 2019 Mar;21(2):142-156. doi: 10.1177/1099800418823286. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Biol Res Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30701989 Free PMC article.
-
ChIP-DIP maps binding of hundreds of proteins to DNA simultaneously and identifies diverse gene regulatory elements.Nat Genet. 2024 Dec;56(12):2827-2841. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-02000-5. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Nat Genet. 2024. PMID: 39587360 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

