Transcriptional control analyses of the Xiphophorus melanoma oncogene
- PMID: 26348392
- PMCID: PMC4662873
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.09.001
Transcriptional control analyses of the Xiphophorus melanoma oncogene
Abstract
Melanoma development in interspecific hybrids of Xiphophorus is induced by the overexpression of the mutationally activated receptor tyrosine kinase Xmrk in pigment cells. Based on the melanocyte specificity of the transcriptional upregulation, a pigment cell-specific promoter region was postulated for xmrk, the activity of which is controlled in healthy purebred fish by the molecularly still unidentified regulator locus R. However, as yet the xmrk promoter region is still poorly characterized. In order to contribute to a better understanding of xmrk expression regulation, we performed a functional analysis of the entire putative gene regulatory region of the oncogene using conventional plasmid-based reporter systems as well as a newly established method employing BAC-derived luciferase reporter constructs in melanoma and non-melanoma cell lines. Using the melanocyte-specific mitfa promoter as control, we could demonstrate that our in vitro system is able to reliably monitor regulation of transcription through cell type-specific regulatory sequences. We found that sequences within 200kb flanking the xmrk oncogene do not lead to any specific transcriptional activation in melanoma compared to control cells. Hence, xmrk reporter constructs fail to faithfully reproduce the endogenous transcriptional regulation of the oncogene. Our data therefore strongly indicate that the melanocyte-specific transcription of xmrk is not the consequence of pigment cell-specific cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region. This hints at additional regulatory mechanisms involved in transcriptional control of the oncogene, thereby suggesting a key role for epigenetic mechanisms in oncogenic xmrk overexpression and thereby in tumor development in Xiphophorus.
Keywords: Cis-regulatory element; EGF receptor; Melanoma; Pigment cell; Transcriptional control; Tumor suppressor; Xiphophorus; xmrk oncogene.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
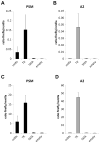



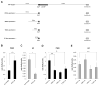
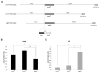
References
-
- Adam D, Dimitrijevic N, Schartl M. Tumor suppression in Xiphophorus by an accidentally acquired promoter. Science. 1993;259:816–819. - PubMed
-
- Adam D, Maueler W, Schartl M. Transcriptional activation of the melanoma inducing Xmrk oncogene in Xiphophorus. Oncogene. 1991;6:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Ahuja MR, Anders F. A Genetic Concept of the Origin of Cancer, based in Part upon Studies of Neoplasms. Fish Prog Exptl Tumor Res. 1976;20:380–397. - PubMed
-
- Altschmied J, Ditzel L, Schartl M. Hypomethylation of the Xmrk oncogene promoter in melanoma cells of Xiphophorus. Biol Chem. 1997;378:1457–1466. - PubMed
-
- Altschmied J, Duschl J. Set of optimized luciferase reporter gene plasmids compatible with widely used CAT vectors. Biotechniques. 1997;23:436–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

