CarD uses a minor groove wedge mechanism to stabilize the RNA polymerase open promoter complex
- PMID: 26349034
- PMCID: PMC4593161
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.08505
CarD uses a minor groove wedge mechanism to stabilize the RNA polymerase open promoter complex
Abstract
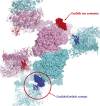
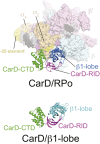
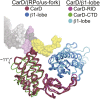
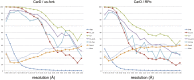
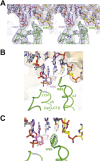
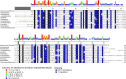
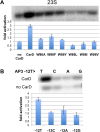
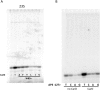
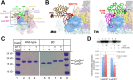
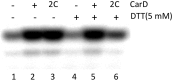
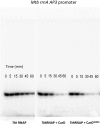
A key point to regulate gene expression is at transcription initiation, and activators play a major role. CarD, an essential activator in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, is found in many bacteria, including Thermus species, but absent in Escherichia coli. To delineate the molecular mechanism of CarD, we determined crystal structures of Thermus transcription initiation complexes containing CarD. The structures show CarD interacts with the unique DNA topology presented by the upstream double-stranded/single-stranded DNA junction of the transcription bubble. We confirm that our structures correspond to functional activation complexes, and extend our understanding of the role of a conserved CarD Trp residue that serves as a minor groove wedge, preventing collapse of the transcription bubble to stabilize the transcription initiation complex. Unlike E. coli RNAP, many bacterial RNAPs form unstable promoter complexes, explaining the need for CarD.
Keywords: CarD; E. coli; RNA polymerase; Thermus aquaticus; X-ray crystallography; biochemistry; biophysics; structural biology; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


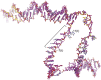



References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

