The identification of an integral membrane, cytochrome c urate oxidase completes the catalytic repertoire of a therapeutic enzyme
- PMID: 26349049
- PMCID: PMC4562309
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13798
The identification of an integral membrane, cytochrome c urate oxidase completes the catalytic repertoire of a therapeutic enzyme
Abstract
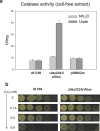
In living organisms, the conversion of urate into allantoin requires three consecutive enzymes. The pathway was lost in hominid, predisposing humans to hyperuricemia and gout. Among other species, the genomic distribution of the two last enzymes of the pathway is wider than that of urate oxidase (Uox), suggesting the presence of unknown genes encoding Uox. Here we combine gene network analysis with association rule learning to identify the missing urate oxidase. In contrast with the known soluble Uox, the identified gene (puuD) encodes a membrane protein with a C-terminal cytochrome c. The 8-helix transmembrane domain corresponds to DUF989, a family without similarity to known proteins. Gene deletion in a PuuD-encoding organism (Agrobacterium fabrum) abolished urate degradation capacity; the phenotype was fully restored by complementation with a cytosolic Uox from zebrafish. Consistent with H2O2 production by zfUox, urate oxidation in the complemented strain caused a four-fold increase of catalase. No increase was observed in the wild-type, suggesting that urate oxidation by PuuD proceeds through cytochrome c-mediated electron transfer. These findings identify a missing link in purine catabolism, assign a biochemical activity to a domain of unknown function (DUF989), and complete the catalytic repertoire of an enzyme useful for human therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Terkeltaub R. Update on gout: new therapeutic strategies and options. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 6, 30–38 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Cheuk D. K. L., Chiang A. K. S., Chan G. C. F. & Ha S. Y. Urate oxidase for the prevention and treatment of tumour lysis syndrome in children with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 8, CD006945 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Roche A. et al. Efficacy of Rasburicase in Hyperuricemia Secondary to Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 53, 677–680 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Ramazzina I., Folli C., Secchi A., Berni R. & Percudani R. Completing the uric acid degradation pathway through phylogenetic comparison of whole genomes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 144–148 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

