Teaching old drugs new tricks to stop malaria invasion in its tracks
- PMID: 26349580
- PMCID: PMC4563855
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-015-0185-6
Teaching old drugs new tricks to stop malaria invasion in its tracks
Abstract
Malaria is a common and life-threatening disease endemic in large parts of the world. The emergence of antimalarial drug resistance is threatening disease-control measures that depend heavily on treatment of clinical malaria. The intracellular malaria parasite is particularly vulnerable during its brief extracellular stage of the life cycle. Wilson et al. describe a screen targeting these extracellular parasite stages and make the surprising discovery that clinically used macrolide antibiotics are potent inhibitors of parasite invasion into erythrocytes.See research article: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7007/13/52.
Figures
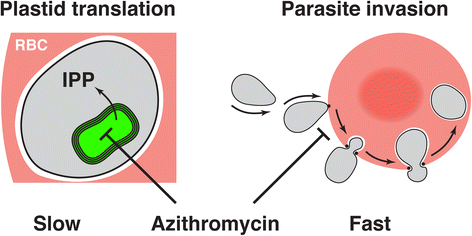
Comment on
-
Macrolides rapidly inhibit red blood cell invasion by the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.BMC Biol. 2015 Jul 18;13:52. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0162-0. BMC Biol. 2015. PMID: 26187647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Malaria Report 2014. Geneva: WHO; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

