Discovery of a series of novel phenylpiperazine derivatives as EGFR TK inhibitors
- PMID: 26349898
- PMCID: PMC4563558
- DOI: 10.1038/srep13934
Discovery of a series of novel phenylpiperazine derivatives as EGFR TK inhibitors
Abstract
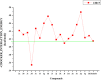
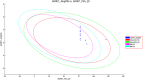
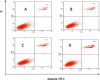
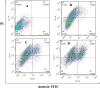
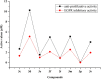
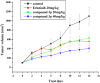
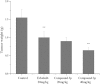
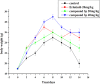
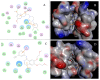
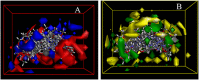
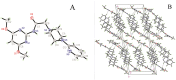
Human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an important drug target that plays a fundamental role in signal transduction pathways in oncology. We report herein the discovery of a novel class of phenylpiperazine derivatives with improved potency toward EGFR. The biological activity of compound 3p as inhibitor of EGFR was further investigated both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, compound 3p exhibited an IC50 in the nanomolar range in A549 cell cultures and induced a cessation of tumor growth with no toxicity, as determined by loss of body weight and death of treated mice. Compoutational docking studies also showed that compound 3p has interaction with EGFR key residues in the active site.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of phenylpiperazine derivatives as IGF-1R inhibitor with potent antiproliferative properties in vitro.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Mar 1;25(5):1067-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25648298
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of thiazolidinone derivatives as potential EGFR and HER-2 kinase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Jan 1;18(1):314-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.10.051. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 19914835
-
RBx10080307, a dual EGFR/IGF-1R inhibitor for anticancer therapy.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jul 5;711(1-3):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.016. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23639757
-
Discovery of 6-substituted 4-anilinoquinazolines with dioxygenated rings as novel EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Sep 15;22(18):5870-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.07.079. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22901387
-
Combined epidermal growth factor receptor targeting with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839) and the monoclonal antibody cetuximab (IMC-C225): superiority over single-agent receptor targeting.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 1;10(19):6487-501. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0870. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15475436
Cited by
-
Cembrene Diterpenoids with Ether Linkages from Sarcophyton ehrenbergi: An Anti-Proliferation and Molecular-Docking Assessment.Mar Drugs. 2017 Jun 21;15(6):192. doi: 10.3390/md15060192. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28635645 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Molecular Docking for the Research and Discovery of Potential Marine Drugs.Mar Drugs. 2020 Oct 30;18(11):545. doi: 10.3390/md18110545. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33143025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined experimental and computational investigation of vildagliptin: spectroscopy, electronic structure, MD and Docking to EGFR, VEGFR2, and HER2 anticancer targets.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2025 Aug 13;39(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s10822-025-00646-9. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2025. PMID: 40802014 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the interaction between epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and some of the synthesized inhibitors using combination of in-silico and in-vitro cytotoxicity methods.Res Pharm Sci. 2018 Dec;13(6):509-522. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.245963. Res Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 30607149 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Novel Dual Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors as Potential Anti-Alzheimer's Disease Agents Using Pharmacophore, 3D-QSAR, and Molecular Docking Approaches.Molecules. 2017 Jul 26;22(8):1254. doi: 10.3390/molecules22081254. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28933746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manning G., Whyte D. B., M artinez R., Hunter T. & Sudarsanam S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science. 298, 1912–1934 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Zuccotto F., Ardini E., Casale E. & Angiolini M. Through the “gatekeeper door”: exploiting the active kinase conformation. J. Med. Chem. 53, 2681–2694 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. Protein kinases-the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 1, 309–315 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Levitzki A. Protein Kinase Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Modality. Acc. Chem. Res. 36, 462–469 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Greenberger L. M. et al. EKB-569: a new irreversible inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase for the treatment of cancer. 11th NCI-EORTC-AACR Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer. Res. 6, 388–389 (2000).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

