RGD-conjugated two-photon absorbing near-IR emitting fluorescent probes for tumor vasculature imaging
- PMID: 26351137
- PMCID: PMC4627496
- DOI: 10.1039/c5ob01536g
RGD-conjugated two-photon absorbing near-IR emitting fluorescent probes for tumor vasculature imaging
Abstract
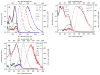
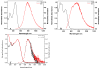
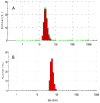
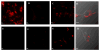
Observation of the activation and inhibition of angiogenesis processes is important in the progression of cancer. Application of targeting peptides, such as a small peptide that contains adjacent L-arginine (R), glycine (G) and L-aspartic acid (D) residues can afford high selectivity and deep penetration in vessel imaging. To facilitate deep tissue vasculature imaging, probes that can be excited via two-photon absorption (2PA) in the near-infrared (NIR) and subsequently emit in the NIR are essential. In this study, the enhancement of tissue image quality with RGD conjugates was investigated with new NIR-emitting pyranyl fluorophore derivatives in two-photon fluorescence microscopy. Linear and nonlinear photophysical properties of the new probes were comprehensively characterized; significantly the probes exhibited good 2PA over a broad spectral range from 700-1100 nm. Cell and tissue images were then acquired and examined, revealing deep penetration and high contrast with the new pyranyl RGD-conjugates up to 350 μm in tumor tissue.
Figures

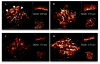
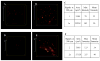
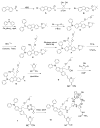
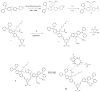
References
-
- Provenzano PP, Eliceiri KW, Keely PJ. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(4):357–370. - PubMed
- Tozer GM, Ameer-Beg SM, Baker J, Barber PR, Hill SA, Hodgkiss RJ, Locke R, Prise VE, Wilson I, Vojnovic B. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2005;57(1):135–152. - PubMed
- Beerling E, Ritsma L, Vrisekoop N, Derksen PWB, van Rheenen J. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(3):299–310. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

