Renovascular hypertension: a case with atypical neurological signs
- PMID: 26351310
- PMCID: PMC4567731
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-208336
Renovascular hypertension: a case with atypical neurological signs
Abstract
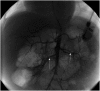
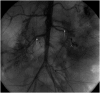
Secondary hypertension is the most frequent form of hypertension in children. Renovascular disease accounts for 5-10% of all childhood hypertension and should be suspected in the presence of severe hypertension found difficult to manage with medical therapy. Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to severe target organ damage. We describe the case of a 13-month-old baby boy with failure to thrive, recent muscular weakness of the lower extremities and irritability. Hypertension was detected and he was admitted to the paediatric intensive care unit with a refractory hypertensive emergency, despite multiple antihypertensive therapies. Bilateral renal artery stenosis was diagnosed through renal angiography and balloon dilation was performed, leading to lower blood pressure. He is currently withdrawing from antihypertensive medication, and slowly gaining weight and recovering from target organ damage. However, weakness of the lower extremities persists and he has been diagnosed with a neurogenic bladder.
2015 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Case report: Bilateral renal artery stenosis in a 7-year-old child.Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2014 Jul-Sep;10(3):190-2. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-10-3-190. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2014. PMID: 25574348 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for renovascular hypertension in a neonate.Acta Paediatr. 2005 Aug;94(8):1149-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2005.tb02061.x. Acta Paediatr. 2005. PMID: 16188865
-
The Dutch Renal Artery Stenosis Intervention Cooperative (DRASTIC) Study: rationale, design and inclusion data.J Hypertens Suppl. 1998 Oct;16(6):S21-7. J Hypertens Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9856380 Clinical Trial.
-
Mid-aortic syndrome: a case report and review of the literature.Int J Cardiol. 2008 Jan 24;123(3):348-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.11.167. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Int J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 17321619 Review.
-
Interventions for pediatric renovascular hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Apr;16(4):422. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0422-3. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 24522941 Review.
References
-
- Sorof JM, Lai D, Turner J et al. . Overweight, ethnicity, and the prevalence of hypertension in school-aged children. Pediatrics 2004;113:475–82. - PubMed
-
- Mattoo TK. Epidemiology, risk factors and hypertension in children and adolescents. http://www.uptodate.com/contents/epidemiology-risk-factors-and-etiology-... (accessed 26 Apr 2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
