Protective Effects of Hydrocortisone, Vitamin C and E Alone or in Combination against Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rat
- PMID: 26351497
- PMCID: PMC4539741
Protective Effects of Hydrocortisone, Vitamin C and E Alone or in Combination against Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rat
Abstract
Background: Renal ischemia reperfusion injury may occur in a variety of clinical situations, following a transient drop in total or regional blood flow to the kidney. This study was performed to investigate the protective effects of different antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, hydrocortisone and combination of these agents against experimental renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Method: Thirty male rats were divided into six groups. Group Sham, Group I/R: (45 min of ischemia followed by 1h of reperfusion), Group I/R+Vit C: (50 mg/kg Vit C, IV, immediately after reperfusion), Group I/R+Vit E: (20 mg/kg Vit E, IM, 15 min before reperfusion), Group I/R+Hydrocortisone: (50 mg/kg, IV, immediately after reperfusion), and Group Combination: Ischemia-reperfusion plus combination of Vit C, E and hydrocortisone. After the experiments, the left kidney was removed and the tissues were processed for histopathological examination.
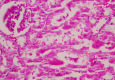
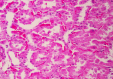
Result: Severe injuries such as necrosis of tubules, atrophy of glomerulus, and hemorrhage were observed in group I/R. Histological scores indicating tissue injury significantly decreased in all treatment groups compared to the group I/R. The renal tissue in group treatment was preserved in comparison with the group I/R. Comparison between the treatment groups showed that group combination was more effective and group vit E was less effective in protecting of renal tissue against I/R injuries.
Conclusion: The results demonstrated simultaneous administration of combination of Vit C, E and hydrocortisone before reperfusion of blood flow to the ischemic tissue could show a synergy against deleterious effects of I/R injuries in kidney.
Keywords: Hydrocortisone; Ischemia; Kidney; Reperfusion; Vitamin C; Vitamin E.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of perfluorooctylbromide and vitamin E on ischemia induced retinal oxidative tissue damage.Exp Eye Res. 1998 Jan;66(1):19-24. doi: 10.1006/exer.1997.0399. Exp Eye Res. 1998. PMID: 9533827
-
The effects of iloprost and vitamin C on kidney as a remote organ after ischemia/reperfusion of lower extremities.J Surg Res. 2007 Jun 1;140(1):20-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.04.031. Epub 2007 Mar 30. J Surg Res. 2007. PMID: 17397869
-
Protective effects of vitamin E against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.Saudi Med J. 2010 Feb;31(2):142-7. Saudi Med J. 2010. PMID: 20174728
-
Cardioprotection from ischemia and reperfusion injury by Withania somnifera: a hemodynamic, biochemical and histopathological assessment.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 May;260(1-2):39-47. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000026051.16803.03. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15228084
-
The protective effects of melatonin and vitamin E against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Ren Fail. 2007;29(5):535-42. doi: 10.1080/08860220701391738. Ren Fail. 2007. PMID: 17654314
Cited by
-
Early Vitamin C, Hydrocortisone, and Thiamine Treatment for Septic Cardiomyopathy: A Propensity Score Analysis.J Pers Med. 2021 Jun 28;11(7):610. doi: 10.3390/jpm11070610. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34203183 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of antioxidants in sepsis-associated oxidative stress: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 6;14:1348713. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1348713. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38510969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrocortisone, Ascorbic Acid and Thiamine (HAT Therapy) for the Treatment of Sepsis. Focus on Ascorbic Acid.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 14;10(11):1762. doi: 10.3390/nu10111762. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30441816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid and thiamine for sepsis: Is the jury out?World J Diabetes. 2020 Apr 15;11(4):90-94. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i4.90. World J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32313607 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin C: should we supplement?Curr Opin Crit Care. 2018 Aug;24(4):248-255. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000510. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 29864039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mejía-Vilet JM, Ramírez V , Cruz C , Uribe N , Gamba G , Bobadilla NA. Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury is prevented by the mineralocorticoid receptor blocker spironolactone. Am J Physiol. 2007;293:78–86. - PubMed
-
- Lakshmanadoss U. Novel Strategies in Ischemic Heart Disease. Croatia: Tech Europ; 2012.
-
- Kelly KJ, Molitoris BA. Acute renal failure in the new millennium: time to consider combination therapy. Semin Nephrol. 2000;20:4–19. - PubMed
-
- Molina A, Ubeda M, Escribese MM, Bermejo LG, Sancho D, Pe´rez de Lema G, et al. Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Functional Tissue Preservation by Anti-Activated _ Integrin Therapy. J Am Sci Nephrol. 2005;16:374–382. - PubMed
-
- Chan KL. Role of Nitric Oxide in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. urrent Medicinal Chemistry - Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents. 1(1):1–13.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
