Quercetin reduces Ehrlich tumor-induced cancer pain in mice
- PMID: 26351625
- PMCID: PMC4550761
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/285708
Quercetin reduces Ehrlich tumor-induced cancer pain in mice
Abstract
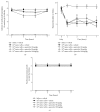
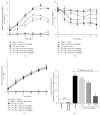
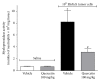
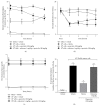
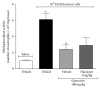
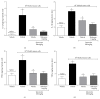
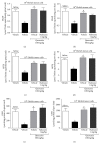
Cancer pain directly affects the patient's quality of life. We have previously demonstrated that the subcutaneous administration of the mammary adenocarcinoma known as Ehrlich tumor induces pain in mice. Several studies have shown that the flavonoid quercetin presents important biological effects, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, analgesic, and antitumor activity. Therefore, the analgesic effect and mechanisms of quercetin were evaluated in Ehrlich tumor-induced cancer pain in mice. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) treatments with quercetin reduced Ehrlich tumor-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia, but not paw thickness or histological alterations, indicating an analgesic effect without affecting tumor growth. Regarding the analgesic mechanisms of quercetin, it inhibited the production of hyperalgesic cytokines IL-1β and TNFα and decreased neutrophil recruitment (myeloperoxidase activity) and oxidative stress. Naloxone (opioid receptor antagonist) inhibited quercetin analgesia without interfering with neutrophil recruitment, cytokine production, and oxidative stress. Importantly, cotreatment with morphine and quercetin at doses that were ineffective as single treatment reduced the nociceptive responses. Concluding, quercetin reduces the Ehrlich tumor-induced cancer pain by reducing the production of hyperalgesic cytokines, neutrophil recruitment, and oxidative stress as well as by activating an opioid-dependent analgesic pathway and potentiation of morphine analgesia. Thus, quercetin treatment seems a suitable therapeutic approach for cancer pain that merits further investigation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tephrosia sinapou ethyl acetate extract inhibits inflammatory pain in mice: opioid receptor dependent inhibition of TNFα and IL-1β production.Pharm Biol. 2013 Oct;51(10):1262-71. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.786099. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Pharm Biol. 2013. PMID: 23855752
-
The Ehrlich tumor induces pain-like behavior in mice: a novel model of cancer pain for pathophysiological studies and pharmacological screening.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:624815. doi: 10.1155/2013/624815. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24073414 Free PMC article.
-
Bosentan, a mixed endothelin receptor antagonist, inhibits superoxide anion-induced pain and inflammation in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;388(11):1211-21. doi: 10.1007/s00210-015-1160-z. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26246053
-
The Phytochemical, Quercetin, Attenuates Nociceptive and Pathological Pain: Neurophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Molecules. 2024 Aug 21;29(16):3957. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163957. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39203035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Emerging Role of Quercetin in the Treatment of Chronic Pain.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;20(12):2346-2353. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220812122437. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35959909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress: A Promising Target for Chemoprevention.Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2016 Apr;2(2):73-81. doi: 10.1007/s40495-016-0052-3. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27088073 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Nrf2 Modulation to the Mechanism of Action of Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Drugs in Pre-clinical and Clinical Stages.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 11;9:1536. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01536. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30687097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent development in antihyperalgesic effect of phytochemicals: anti-inflammatory and neuro-modulatory actions.Inflamm Res. 2018 Aug;67(8):633-654. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1156-5. Epub 2018 May 16. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29767332 Review.
-
An Investigation of the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Analgesic Effect of Jakyak-Gamcho Decoction: A Network Pharmacology Study.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Dec 1;2020:6628641. doi: 10.1155/2020/6628641. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33343676 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Oxidative Stress, Autophagy, and Apoptosis by Quercetin to Ameliorate Cisplatin-induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Rats.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2023 Jan 5;11(2):107-114. doi: 10.4103/jmau.jmau_78_22. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2023. PMID: 37448816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hearn J., Higginson I. J. Cancer pain epidemiology: a systematic review. In: Bruera E. D., Portenoy R. K., editors. Cancer Pain: Assessment and Management. London, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2003. pp. 19–37.
-
- Regan J. M., Peng P. Neurophysiology of cancer pain. Cancer Control. 2000;7(2):111–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

