Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Ameliorates Endothelial Dysfunction in Radiation-Induced Bladder Injury
- PMID: 26351640
- PMCID: PMC4550748
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/967680
Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Ameliorates Endothelial Dysfunction in Radiation-Induced Bladder Injury
Abstract
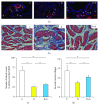
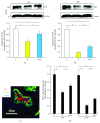
This study was designed to explore the effect of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on radiation-induced endothelial dysfunction and histological changes in the urinary bladder. bFGF was administrated to human umbilical vein cells (HUVEC) or urinary bladder immediately after radiation. Reduced expression of thrombomodulin (TM) was indicated in the HUVEC and urinary bladder after treatment with radiation. Decreased apoptosis was observed in HUVEC treated with bFGF. Administration of bFGF increased the expression of TM in HUVEC medium, as well as in the urinary bladder at the early and delayed phases of radiation-induced bladder injury (RIBI). At the early phase, injection of bFGF increased the thickness of urothelium and reduced inflammation within the urinary bladder. At the delayed phase, bFGF was effective in reducing fibrosis within the urinary bladder. Our results indicate that endothelial dysfunction is a prominent feature of RIBI. Administration of bFGF can ameliorate radiation-induced endothelial dysfunction in urinary bladder and preserve bladder histology at early and delayed phases of RIBI.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of transforming growth factor beta1 gene, basic fibroblast growth factor gene and hydroxyproline in diabetes-induced bladder dysfunction in a rat model.Neurourol Urodyn. 2008;27(3):254-9. doi: 10.1002/nau.20489. Neurourol Urodyn. 2008. PMID: 17763394
-
Atherosclerosis-induced chronic ischemia causes bladder fibrosis and non-compliance in the rabbit.J Urol. 1999 May;161(5):1626-35. J Urol. 1999. PMID: 10210430
-
[The role of structural changes of the urinary bladder extracellular matrix in the occurrence of different grades of adverse events after radiation therapy].Urologiia. 2018 May;(2):14-19. Urologiia. 2018. PMID: 29901289 Russian.
-
Significance of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of early and delayed radiation enteropathy.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jun 14;13(22):3047-55. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i22.3047. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17589919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation injury and the protein C pathway.Crit Care Med. 2004 May;32(5 Suppl):S325-30. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000126358.15697.75. Crit Care Med. 2004. PMID: 15118539 Review.
Cited by
-
X‑irradiation induces acute and early term inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis‑prone ApoE‑/‑ mice and in endothelial cells.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jun;23(6):399. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12038. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33786610 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of myeloablative radiation on urinary bladder mast cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 14;14(1):6219. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56655-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38485999 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion Molecules ICAM-1 and PECAM-1 as Potential Biomarkers of Central Nervous System Damage in Women Breast Cancer Survivors.Pathophysiology. 2022 Feb 16;29(1):52-65. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology29010006. Pathophysiology. 2022. PMID: 35366289 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of the vascular endothelial barrier in the immune-inflammatory response induced by radiotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2018 Sep;91(1089):20170762. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170762. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29630386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Effect of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Radiation-Induced Bladder Injury.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3679047. doi: 10.1155/2016/3679047. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27051426 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

