Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells against CD19 for Multiple Myeloma
- PMID: 26352815
- PMCID: PMC4646711
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504542
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells against CD19 for Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
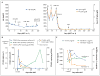
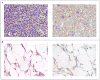
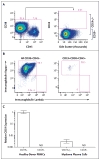
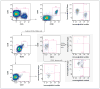
A patient with refractory multiple myeloma received an infusion of CTL019 cells, a cellular therapy consisting of autologous T cells transduced with an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor, after myeloablative chemotherapy (melphalan, 140 mg per square meter of body-surface area) and autologous stem-cell transplantation. Four years earlier, autologous transplantation with a higher melphalan dose (200 mg per square meter) had induced only a partial, transient response. Autologous transplantation followed by treatment with CTL019 cells led to a complete response with no evidence of progression and no measurable serum or urine monoclonal protein at the most recent evaluation, 12 months after treatment. This response was achieved despite the absence of CD19 expression in 99.95% of the patient's neoplastic plasma cells. (Funded by Novartis and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02135406.).
Figures
Comment in
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Myeloma.N Engl J Med. 2016 Jan 14;374(2):194. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1512760. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 26760100 No abstract available.
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Myeloma.N Engl J Med. 2016 Jan 14;374(2):193-4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1512760. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 26760101 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
