Blood coagulation protein fibrinogen promotes autoimmunity and demyelination via chemokine release and antigen presentation
- PMID: 26353940
- PMCID: PMC4579523
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9164
Blood coagulation protein fibrinogen promotes autoimmunity and demyelination via chemokine release and antigen presentation
Abstract
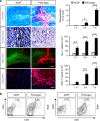
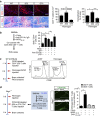
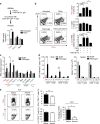
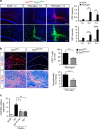
Autoimmunity and macrophage recruitment into the central nervous system (CNS) are critical determinants of neuroinflammatory diseases. However, the mechanisms that drive immunological responses targeted to the CNS remain largely unknown. Here we show that fibrinogen, a central blood coagulation protein deposited in the CNS after blood-brain barrier disruption, induces encephalitogenic adaptive immune responses and peripheral macrophage recruitment into the CNS leading to demyelination. Fibrinogen stimulates a unique transcriptional signature in CD11b(+) antigen-presenting cells inducing the recruitment and local CNS activation of myelin antigen-specific Th1 cells. Fibrinogen depletion reduces Th1 cells in the multiple sclerosis model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) II-dependent antigen presentation, CXCL10- and CCL2-mediated recruitment of T cells and macrophages, respectively, are required for fibrinogen-induced encephalomyelitis. Inhibition of the fibrinogen receptor CD11b/CD18 protects from all immune and neuropathologic effects. Our results show that the final product of the coagulation cascade is a key determinant of CNS autoimmunity.
Figures



References
-
- Davalos D. & Akassoglou K. Fibrinogen as a key regulator of inflammation in disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 34, 43–62 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Vos C. M. et al. Blood-brain barrier alterations in both focal and diffuse abnormalities on postmortem MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 20, 953–960 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL102475/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096126/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL096126/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA082103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073737/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD000850/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052189/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063008/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA082103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD072222/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102475/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

