Hypertriglyceridemia is a major factor associated with elevated levels of small dense LDL cholesterol in patients with metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 26354346
- PMCID: PMC4579102
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.586
Hypertriglyceridemia is a major factor associated with elevated levels of small dense LDL cholesterol in patients with metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Background: We aimed to determine the major contributing component of metabolic syndrome (MetS) that results in an elevated small dense LDL cholesterol (sdLDL-C) concentration and sdLDL-C/LDL-C ratio.
Methods: Four hundred and forty-seven subjects (225 men; 222 women) with MetS were randomly selected from the Korean Metabolic Syndrome Research Initiatives-Seoul cohort study. Age- and sex-matched healthy controls (181 men; 179 women) were also randomly selected from the same cohort.
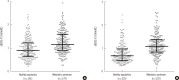
Results: A comparison of the median values of the sdLDL-C concentration between subgroups, divided according to whether subjects met or did not meet the criteria for each MetS component in patients with MetS, revealed a significant difference in the sdLDL-C concentration only between subgroups divided according to whether subjects met or did not meet the triglyceride (TG) criteria (P<0.05 for each gender). The TG level showed a good correlation with sdLDL-C concentration (correlation coefficients [r]=0.543 for men; 0.653 for women) and the sdLDL-C/LDL-C ratio (r=0.789 for men; 0.745 for women). Multiple linear regression analyses conducted for the MetS group concordantly identified TG as one of the most significant contributors to sdLDL-C concentration (β=0.1747±0.0105, P<0.0001) and the sdLDL-C/LDL-C ratio (β=6.9518±0.3011, P<0.0001).
Conclusions: Among five MetS components, only the abnormal TG level was a differentiating factor for sdLDL-C concentration and sdLDL-C/LDL-C ratio. These results were reproducible in both genders, with or without MetS.
Keywords: Hypertriglyceridemia; Metabolic syndrome; Small dense LDL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Smith SC, Jr, Benjamin EJ, Bonow RO, Braun LT, Creager MA, Franklin BA, et al. AHA/ACCF Secondary Prevention and Risk Reduction Therapy for Patients with Coronary and other Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease: 2011 update: a guideline from the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology Foundation. Circulation. 2011;124:2458–2473. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB, Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation. 2004;110:227–239. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB. Range of serum cholesterol values in the population developing coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1995;76:69C–77C. - PubMed
-
- Grundy SM. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2595–2600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

