A Reassessment of IgM Memory Subsets in Humans
- PMID: 26355154
- PMCID: PMC4594759
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500753
A Reassessment of IgM Memory Subsets in Humans
Abstract
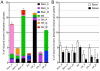
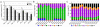
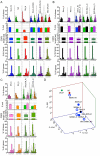
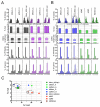
From paired blood and spleen samples from three adult donors, we performed high-throughput VH sequencing of human B cell subsets defined by IgD and CD27 expression: IgD(+)CD27(+) ("marginal zone [MZ]"), IgD(-)CD27(+) ("memory," including IgM ["IgM-only"], IgG and IgA) and IgD(-)CD27(-) cells ("double-negative," including IgM, IgG, and IgA). A total of 91,294 unique sequences clustered in 42,670 clones, revealing major clonal expansions in each of these subsets. Among these clones, we further analyzed those shared sequences from different subsets or tissues for VH gene mutation, H-CDR3-length, and VH/JH usage, comparing these different characteristics with all sequences from their subset of origin for which these parameters constitute a distinct signature. The IgM-only repertoire profile differed notably from that of MZ B cells by a higher mutation frequency and lower VH4 and higher JH6 gene usage. Strikingly, IgM sequences from clones shared between the MZ and the memory IgG/IgA compartments showed a mutation and repertoire profile of IgM-only and not of MZ B cells. Similarly, all IgM clonal relationships (among MZ, IgM-only, and double-negative compartments) involved sequences with the characteristics of IgM-only B cells. Finally, clonal relationships between tissues suggested distinct recirculation characteristics between MZ and switched B cells. The "IgM-only" subset (including cells with its repertoire signature but higher IgD or lower CD27 expression levels) thus appear as the only subset showing precursor-product relationships with CD27(+) switched memory B cells, indicating that they represent germinal center-derived IgM memory B cells and that IgM memory and MZ B cells constitute two distinct entities.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

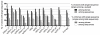
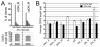

Similar articles
-
Differential Expression of IgM and IgD Discriminates Two Subpopulations of Human Circulating IgM+IgD+CD27+ B Cells That Differ Phenotypically, Functionally, and Genetically.Front Immunol. 2020 May 6;11:736. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00736. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32435242 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for preferential Ig gene usage and differential TdT and exonuclease activities in human naïve and memory B cells.Mol Immunol. 2007 Mar;44(9):2173-83. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.11.020. Epub 2006 Dec 29. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17196657 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular footprints of a germinal center derivation of human IgM+(IgD+)CD27+ B cells and the dynamics of memory B cell generation.J Exp Med. 2009 Nov 23;206(12):2659-69. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091087. Epub 2009 Nov 16. J Exp Med. 2009. PMID: 19917772 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of Memory Marginal Zone B Cells.Crit Rev Immunol. 2018;38(2):145-158. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2018024985. Crit Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29887727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[IgM+IgD+CD27+ B cells in human: an essential role in the protection against encapsulated bacteria].Med Sci (Paris). 2015 Jun-Jul;31(6-7):647-53. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20153106018. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Med Sci (Paris). 2015. PMID: 26152169 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Plasmodium falciparum-specific IgM B cells dominate in children, expand with malaria, and produce functional IgM.J Exp Med. 2021 Apr 5;218(4):e20200901. doi: 10.1084/jem.20200901. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 33661303 Free PMC article.
-
Checkpoints for Autoreactive B Cells in the Peripheral Blood of Lupus Patients Assessed by Flow Cytometry.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Sep;68(9):2210-20. doi: 10.1002/art.39710. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27059652 Free PMC article.
-
Repertoire comparison of the B-cell receptor-encoding loci in humans and rhesus macaques by next-generation sequencing.Clin Transl Immunology. 2016 Jul 22;5(7):e93. doi: 10.1038/cti.2016.42. eCollection 2016 Jul. Clin Transl Immunology. 2016. PMID: 27525066 Free PMC article.
-
Innate B Cells: the Archetype of Protective Immune Cells.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020 Feb;58(1):92-106. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08748-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31183788 Review.
-
Toll-like receptor 9 stimulation can induce IκBζ expression and IgM secretion in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.Haematologica. 2017 Nov;102(11):1901-1912. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.165878. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 28775123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dogan I, Bertocci B, Vilmont V, Delbos F, Megret J, Storck S, Reynaud CA, Weill JC. Multiple layers of B cell memory with different effector functions. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:1292–1299. - PubMed
-
- Balazs M, Martin F, Zhou T, Kearney J. Blood dendritic cells interact with splenic marginal zone B cells to initiate T-independent immune responses. Immunity. 2002;17:341–352. - PubMed
-
- Wirths S, Lanzavecchia A. ABCB1 transporter discriminates human resting naive B cells from cycling transitional and memory B cells. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:3433–3441. - PubMed
-
- Fecteau JF, G Cote,, Neron S. A new memory CD27-IgG+ B cell population in peripheral blood expressing VH genes with low frequency of somatic mutation. J Immunol. 2006;177:3728–3736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

