IFN-γ Prevents Adenosine Receptor (A2bR) Upregulation To Sustain the Macrophage Activation Response
- PMID: 26355158
- PMCID: PMC4686143
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501139
IFN-γ Prevents Adenosine Receptor (A2bR) Upregulation To Sustain the Macrophage Activation Response
Abstract
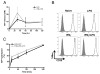
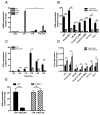
The priming of macrophages with IFN-γ prior to TLR stimulation results in enhanced and prolonged inflammatory cytokine production. In this study, we demonstrate that, following TLR stimulation, macrophages upregulate the adenosine 2b receptor (A2bR) to enhance their sensitivity to immunosuppressive extracellular adenosine. This upregulation of A2bR leads to the induction of macrophages with an immunoregulatory phenotype and the downregulation of inflammation. IFN-γ priming of macrophages selectively prevents the induction of the A2bR in macrophages to mitigate sensitivity to adenosine and to prevent this regulatory transition. IFN-γ-mediated A2bR blockade leads to a prolonged production of TNF-α and IL-12 in response to TLR ligation. The pharmacologic inhibition or the genetic deletion of the A2bR results in a hyperinflammatory response to TLR ligation, similar to IFN-γ treatment of macrophages. Conversely, the overexpression of A2bR on macrophages blunts the IFN-γ effects and promotes the development of immunoregulatory macrophages. Thus, we propose a novel mechanism whereby IFN-γ contributes to host defense by desensitizing macrophages to the immunoregulatory effects of adenosine. This mechanism overcomes the transient nature of TLR activation, and prolongs the antimicrobial state of the classically activated macrophage. This study may offer promising new targets to improve the clinical outcome of inflammatory diseases in which macrophage activation is dysregulated.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A2B adenosine receptor blockade enhances macrophage-mediated bacterial phagocytosis and improves polymicrobial sepsis survival in mice.J Immunol. 2011 Feb 15;186(4):2444-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001567. Epub 2011 Jan 17. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21242513 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-gamma up-regulates the A2B adenosine receptor expression in macrophages: a mechanism of macrophage deactivation.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 15;162(6):3607-14. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10092821
-
Activation of murine macrophages by Neisseria meningitidis and IFN-gamma in vitro: distinct roles of class A scavenger and Toll-like pattern recognition receptors in selective modulation of surface phenotype.J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Sep;76(3):577-84. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0104014. Epub 2004 Jun 24. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15218052
-
Regulation of interferon and Toll-like receptor signaling during macrophage activation by opposing feedforward and feedback inhibition mechanisms.Immunol Rev. 2008 Dec;226:41-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00707.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19161415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic Signaling to Terminate TLR Responses in Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2016 Mar 2;7:74. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00074. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26973651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine Signaling in Mast Cells and Allergic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 14;22(10):5203. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105203. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cluster of Differentiation 39 (CD39) and Purinergic Signaling Pathway in Viral Infections.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 8;12(2):279. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020279. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36839551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunosuppressive adenosine-targeted biomaterials for emerging cancer immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 25;13:1012927. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012927. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The adenosine pathway in immuno-oncology.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Oct;17(10):611-629. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0382-2. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32514148 Review.
-
On the mechanism of anti-CD39 immune checkpoint therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Feb;8(1):e000186. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000186. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32098829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hasko G, Kuhel DG, Chen JF, Schwarzschild MA, Deitch EA, Mabley JG, Marton A, Szabo C. Adenosine inhibits IL-12 and TNF-[alpha] production via adenosine A2a receptor-dependent and independent mechanisms. FASEB J. 2000;14:2065–2074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

