Non-pharmacological interventions for people with epilepsy and intellectual disabilities
- PMID: 26355236
- PMCID: PMC7265116
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005502.pub3
Non-pharmacological interventions for people with epilepsy and intellectual disabilities
Abstract
Background: Approximately 30% of patients with epilepsy remain refractory to drug treatment and continue to experience seizures whilst taking one or more antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Several non-pharmacological interventions that may be used in conjunction with or as an alternative to AEDs are available for refractory patients. In view of the fact that seizures in people with intellectual disabilities are often complex and refractory to pharmacological interventions, it is evident that good quality randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are needed to assess the efficacy of alternatives or adjuncts to pharmacological interventions.This is an updated version of the original Cochrane review (Beavis 2007) published in The Cochrane Library (2007, Issue 4).
Objectives: To assess data derived from randomised controlled trials of non-pharmacological interventions for people with epilepsy and intellectual disabilities.Non-pharmacological interventions include, but are not limited to, the following.• Surgical procedures.• Specialised diets, for example, the ketogenic diet, or vitamin and folic acid supplementation.• Psychological interventions for patients or for patients and carers/parents, for example, cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), electroencephalographic (EEG) biofeedback and educational intervention.• Yoga.• Acupuncture.• Relaxation therapy (e.g. music therapy).
Search methods: For the latest update of this review, we searched the Cochrane Epilepsy Group Specialised Register (19 August 2014), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) via CRSO (19 August 2014), MEDLINE (Ovid, 1946 to 19 August 2014) and PsycINFO (EBSCOhost, 1887 to 19 August 2014).
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials of non-pharmacological interventions for people with epilepsy and intellectual disabilities.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently applied the inclusion criteria and extracted study data.
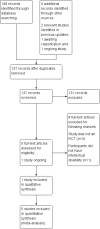
Main results: One study is included in this review. When two surgical procedures were compared, results indicated that corpus callosotomy with anterior temporal lobectomy was more effective than anterior temporal lobectomy alone in improving quality of life and performance on IQ tests among people with epilepsy and intellectual disabilities. No evidence was found to support superior benefit in seizure control for either intervention. This is the only study of its kind and was rated as having an overall unclear risk of bias. The previous update (December 2010) identified one RCT in progress. The study authors have confirmed that they are aiming to publish by the end of 2015; therefore this study (Bjurulf 2008) has not been included in the current review.
Authors' conclusions: This review highlights the need for well-designed randomised controlled trials conducted to assess the effects of non-pharmacological interventions on seizure and behavioural outcomes in people with intellectual disabilities and epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Update of
-
Non-pharmacological interventions for epilepsy in people with intellectual disabilities.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD005502. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005502.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 10;(9):CD005502. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005502.pub3. PMID: 17943860 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Liang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Liang S, Li A, Zhao M, Jiang H, Meng X, Sun Y. Anterior temporal lobectomy combined with anterior corpus callosotomy in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and mental retardation. Seizure 2010;19(6):330‐4. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Amar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Amar AP, Heck CN, Levy ML, Smith T, DeGiorgio CM, Oviedo S. An institutional experience with cervical vagus nerve trunk stimulation for medically refractory epilepsy: rationale, technique, and outcome. Neurosurgery 1998;43(6):1265‐76. - PubMed
-
- Giorgio CM, Schachter SC, Hadfort A, Salinsky M, Thompson J, Uthman B, et al. Prospective long‐term study of vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of refractory seizures. Epilepsia 2000;41:1195‐200. - PubMed
Ben‐Menachem 1994 {published data only}
-
- Ben‐Menachem E, Mañon‐Espaillat R, Ristanovic R, Wilder BJ, Stefan H, Mirza W. Vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of partial seizures: 1. A controlled study of effect on seizures. First International Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group. Epilepsia 1994;35(3):616‐26. - PubMed
Bergqvist 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bergqvist AG, Schall JI, Gallagher PR, Cnaan A, Stallings VA. Fasting versus gradual initiation of the ketogenic diet: a prospective, randomized clinical trial of efficacy. Epilepsia 2005;46(11):1810‐9. - PubMed
Clarke 1997A {published data only}
-
- Clarke BM, Upton AR, Griffin H, Fitzpatrick D, DeNardis M. Chronic stimulation of the left vagus nerve: cognitive motor effects. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1997;24(3):226‐9. - PubMed
Clarke 1997B {published data only}
-
- Clarke BM, Upton AR, Griffin H, Fitzpatrick D, DeNardis M. Seizure control after stimulation of the vagus nerve: clinical outcome measures. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1997;24(3):222‐5. - PubMed
Cross 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cross JH. The ketogenic diet in the treatment of Lennox‐Gastaut syndrome. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2012;54(5):394‐5. - PubMed
Dahl 1985 {published data only}
-
- Dahl J, Melin L, Brorson LO, Schollin J. Effects of a broad‐spectrum behavior modification treatment program on children with refractory epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 1985;26(4):303‐9. - PubMed
Dahl 1987 {published data only}
-
- Dahl J, Melin L, Lund L. Effects of a contingent relaxation treatment program on adults with refractory epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 1987;28(2):125‐32. - PubMed
Dave 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dave UP, Chauvan V, Dalvi J. Evaluation of BR‐16 A (Mentat) in cognitive and behavioural dysfunction of mentally retarded children ‐ a placebo‐controlled study. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1993;60(3):423‐8. - PubMed
Deepak 1994 {published data only}
-
- Deepak KK, Manchanda SK, Maheshwari MC. Meditation improves clinicoelectroencephalographic measures in drug‐resistant epileptics. Biofeedback & Self Regulation 1994;19(1):25‐40. - PubMed
DeGiorgio 1997 {published data only}
-
- Degiorgio C, Heck C, Smith T, Duffell W. Randomised double‐blind study of vagus nerve stimulation in intractable partial seizures. The USC experience and the EUS Study Group. Epilepsia 1997;38(S3):245.
DeGiorgio 2005 {published data only}
-
- DeGiorgio C, Heck C, Bunch S, Britton J, Green P, Lancman M, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy: randomized comparison of three stimulation paradigms. Neurology 2005;65(2):317‐9. - PubMed
Dodrill 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dodrill CB, Morris GL. Effects of vagal nerve stimulation on cognition and quality of life in epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior 2001;2(1):46‐53. - PubMed
Elger 2000 {published data only}
-
- Elger G, Hoppe C, Falkai P, Rush AJ, Elger CE. Vagus nerve stimulation is associated with mood improvements in epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Research 2000;42(2‐3):203‐10. - PubMed
Engelberts 2002 {published data only}
-
- Engelberts NH, Klein M, Adèr HJ, Heimans JJ, Trenité DG, Ploeg HM. The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation for attention deficits in focal seizures: a randomized controlled study. Epilepsia 2002;43(6):587‐95. - PubMed
Freeman 2009a {published data only}
-
- Freeman JM, Vining EPG, Kossoff EH, Pyzik PL, Ye X, Goodman SN. A blinded, crossover study of the efficacy of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 2009;50(2):322‐5. - PubMed
Gates 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gates JR, Liow K, Granner M, Louis E, Leroy R, Albers L, et al. Vagus nerve stimulator (VNS) parameter settings: high stimulation vs low stimulation. Epilepsia 2005;46(S8):223.
Handforth 1998 {published data only}
-
- Handforth A, DeGiorgio CM, Schachter SC, Uthman BM, Naritoku DK, Tecoma ES, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation therapy for partial‐onset seizures: a randomized active‐control trial. Neurology 1998;51(1):48‐55. - PubMed
Helgeson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Helgeson DC, Mittan R, Tan SY, Chayasirisobhon S. Sepulveda Epilepsy Education: the efficacy of a psychoeducational treatment program in treating medical and psychosocial aspects of epilepsy. Epilepsia 1990;31(1):75‐82. - PubMed
Helmstaedter 2011 {published data only}
-
- Helmstaedter C, Roeske S, Kaaden S, Elger CE, Schramm J. Hippocampal resection length and memory outcome in selective epilepsy surgery. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, & Psychiatry 2011;82(12):1375‐81. - PubMed
Hermann 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hermann BP, Wyler AR, Somes G, Peterson J, Clement L. Randomized clinical trial of partial versus total hippocampectomy for treatment of intractable temporal lobe epilepsy: memory outcome. Epilepsia 1993;34(S6):109.
Holder 1992 {published data only}
-
- Holder LK, Wernicke JF, Tarver WB. Treatment of refractory partial seizures: preliminary results of a controlled study. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology 1992;15(10 pt 2):1557‐71. - PubMed
Inuzuka 2005 {published data only}
-
- Inuzuka L, Bustamante VCT, Funayama SS, Bianchin MM, Rosset SRE, Machado HR, et al. Ketogenic diet: clinical and neurophysiological findings in refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 2005;46(S8):28.
Kockelmann 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kockelmann E, Richter S, Thulke S, Schramm J, Helmstaedter C. Effect of mesial pathology and extent of resection on seizure and memory outcome after selective amygdala‐hippocampectomy (SAH). Epilepsia 2005;46(S6):328.
Koubeisse 2013 {published data only}
-
- Koubeissi MZ, Kahriman E, Syed TU, Miller J, Durand DM. Low‐frequency electrical stimulation of fiber tract in temporal lobe epilepsy. Annals of Neurology 2013;74(2):223‐31. - PubMed
Landy 1993 {published data only}
-
- Landy HJ, Ramsay RE, Slater J, Casiano RR, Morgan R. Vagus nerve stimulation for complex partial seizures: surgical technique, safety, and efficacy. Journal of Neurosurgery 1993;78(1):26‐31. - PubMed
Lemmon 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lemmon ME, Terao NN, NG Y‐T, Reisig W, Rubenstein JE, Kossoff EH. Efficacy of the ketogenic diet in Lennox‐Gastaut syndrome: a retrospective review of one institution's experience and summary of the literature. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2012;54(5):464‐8. - PubMed
Liu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Liu S‐Y, An N, Fang X, Singh P, Oommen J, Yin Q, et al. Surgical treatment of patients with Lennox‐Gastaut syndrome phenotype. Neurology 2011;77(15):1473‐81.
Lutz 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lutz MT, Clusmann H, Elger CE, Schramm J, Helmstaedter C. Neuropsychological outcome after selective amygdalohippocampectomy with transsylvian versus transcortical approach: a randomized prospective clinical trial of surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2004;45(7):809‐16. - PubMed
Olley 2001 {published data only}
-
- Olley BO, Osinowo HO, Brieger WR. Psycho‐educational therapy among Nigerian adult patients with epilepsy: a controlled outcome study. Patient Education and Counseling 2001;42(1):25‐33. - PubMed
Panjwani 1987 {published data only}
-
- Panjwani U, Selvamurthy W, Singh SH, Gupta HL, Thakur L, Rai UC. Effect of Sahaja yoga practice on seizure control & EEG changes in patients of epilepsy. Indian Journal of Medical Research 1987;103:165‐72. - PubMed
Puskarich 1992 {published data only}
-
- Puskarich CA, Whitman S, Dell J, Hughes JR, Rosen AJ, Hermann BP. Controlled examination of effects of progressive relaxation training on seizure reduction. Epilepsia 1992;33(4):675‐80. - PubMed
Ramsay 1994 {published data only}
-
- Ramsay RE, Uthman BM, Augustinsson LE, Upton AR, Naritoku D, Willis J. Vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of partial seizures: 2. Safety, side effects, and tolerability. First International Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group. Epilepsia 1994;35(3):627‐36. - PubMed
Scherrmann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Scherrmann J, Hoppe C, Kral T, Schramm J, Elger CE. Vagus nerve stimulation: clinical experience in a large patient series. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology 2001;18(5):408‐14. - PubMed
Sidorenko 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sidorenko VN. Effects of the Medical Resonance Therapy Music in the complex treatment of epileptic patients. Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 2000;35(3):212‐7. - PubMed
Tan 1986 {published data only}
-
- Tan SY, Bruni J. Cognitive‐behavior therapy with adult patients with epilepsy: a controlled outcome study. Epilepsia 1986;27(3):225‐33. - PubMed
VNS Study Group 1995 {published data only}
-
- The Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group. A randomized controlled trial of chronic vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of medically intractable seizures. The Vagus Nerve Stimulation Study Group. Neurology 1995;45(2):224‐30. - PubMed
Warner 1997 {published data only}
-
- Warner MH, Anderson GD, McCarty JP, Farwell JR. Effect of carnitine on measures of energy levels, mood, cognition, and sleep in adolescents with epilepsy treated with valproate. Journal of Epilepsy 1997;10(3):126‐30.
Wu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wu Y, Zou LP, Han TL, Zheng H, Caspi O, Wong V, et al. Randomized controlled trial of traditional Chinese medicine (acupuncture and tuina) in cerebral palsy: Part 1 ‐ Any increase in seizure in integrated acupuncture and rehabilitation group versus rehabilitation group?. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2008;14(8):1005‐9. - PubMed
Wyler 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wyler AR, Hermann BP, Somes G. Extent of medial temporal resection on outcome from anterior temporal lobectomy: a randomized prospective study. Neurosurgery 1995;37(5):982‐90. - PubMed
Yuen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yuen AW, Sander JW, Fluegel D, Patsalos PN, Bell GS, Johnson T. Omega‐3 fatty acid supplementation in patients with chronic epilepsy: a randomized trial. Epilepsy & Behavior 2005;7(2):253‐8. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Bjurulf 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bjurulf B. Comparing ketogenic diet with the most appropriate antiepileptic drug ‐ a randomised study of children with mental retardation and drug resistant epilepsy. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct/show/NCT00552526 (03/10/14).
Additional references
Anand 1991
-
- Anand BK. Yoga and medical science. Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 1991;35(2):84‐7. - PubMed
Bowley 2000
-
- Bowley C, Kerr M. Epilepsy and intellectual disability. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 2000;44(5):529‐43. - PubMed
Cockerell 1997
-
- Cockerell OC, Johnson AL, Sander J, Shorvon SD. Prognosis of epilepsy: a review and further analysis of the first nine years of the British National General Practice Study of Epilepsy, a prospective population‐based study. Epilepsia 1997;38(1):31‐46. - PubMed
Commission 1981
-
- Commission on Classification and Terminology of the ILAE: proposal for revised clinical and EEG classification of epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 1981;22:489‐501. - PubMed
Commission 1989
-
- Commission on Classification and Terminology of the ILAE: proposal for revised classification of epilepsies and epileptic syndromes. Epilepsia 1989;30:389‐99. - PubMed
Engel 2003
-
- Engel J, Wiebe S, French J, Sperling MR, Williamson P, Spencer D, et al. Practice parameter: temporal lobe and localised neocortical resections for epilepsy. Neurology 2003;60:538‐47. - PubMed
Fenwick 1992
-
- Fenwick P. The relationship between mind, brain and seizures. Epilepsia 1992;33(6):1‐6. - PubMed
Freeman 1998
-
- Freeman JM, Vining EPG, Pillas DJ, Pyzik PL, Casey JC, Kelly LM. The efficacy of the ketogenic diet‐‐1998: a prospective evaluation of intervention in 150 children. Pediatrics 1998;102(6):1358‐63. - PubMed
Freeman 2009b
-
- Freeman JM. The ketogenic diet: additional information from crossover study. Journal of Child Neurology 2009;24(4):509‐12. - PubMed
Gleissner 1999
-
- Gleissner U, Johanson K, Helmstaedter C, Elger CE. Surgical outcome in a group of low‐IQ patients with focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 1999;40(5):553‐9. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Hartman 2007
Hemingway 2001
-
- Hemingway C, Freeman JM, Pillas DJ, Pyzik PL. The ketogenic diet: a 3‐ to 6‐year follow‐up of 150 children enrolled prospectively. Pediatrics 2001;108(4):898‐905. - PubMed
Hermann 1999
-
- Hermann B, Davies K, Foley K, Bell B. Visual confrontation naming outcome after standard left anterior temporal lobectomy with sparing versus resection of the superior temporal gyrus: a randomised prospective clinical trial. Epilepsia 1999;40:1070‐6. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011.
Jalilian 2010
-
- Jalilian L, Limbrick DD, Steger‐May K, Johnston J, Powers AK, Smyth MD. Complete versus anterior two‐thirds corpus callosotomy in children: analysis of outcome. Journal of Neurosurgery: Paediatrics 2010;6(3):257‐66. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
-
- Kirkham JJ, Swan KM, Altman DG, Gamble C, Dodd S, Smyth R, et al. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010;340:365. - PubMed
Kloster 1999
-
- Kloster R, Larsson PG, Lossius R, Nakken KO, Dahl R, Xue XL, et al. The effect of acupuncture in chronic intractable epilepsy. Seizure 1999;8(3):170‐4. - PubMed
Kobau 2013
-
- Kobau R, Yao‐Hua L, Zack M, Helmers S, Thurman D. Epilepsy in adults and access to care: United States, 2010. JAMA 2013;309(3):224‐6.
Lefebvre 2009
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Levy 2012
Liang 2014
Lundgren 2008
-
- Lundgren T, Dahl J, Yardi N, Melin I. Acceptance and commitment therapy and yoga for drug‐refractory epilepsy: a randomised controlled trial. Epilepsy & Behavior 2008;13:102‐8. - PubMed
Maciocia 1989
-
- Maciocia G. The Foundations of Chinese Medicine. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone, 1989.
Miller 1994
-
- Miller L. Psychotherapy of epilepsy: seizure control and psychosocial adjustment. Journal of Cognitive Rehabilitation 1994;12:14‐30.
Morgan 2003
-
- Morgan CL, Baxter H, Kerr MP. Prevalence of epilepsy and associated health service utilization and mortality among patients with intellectual disability. American Journal of Mental Retardation 2003;108:293‐300. - PubMed
Panebianco 2015
Panjwani 1996
-
- Panjwani U, Selvamurthy W, Singh SH, Gupta HL Thankur I, Rai UC. Effect of Sahaja yoga practice on seizure control and EEG changes in patients of epilepsy. Indan Journal of Medical Records 1996;103:165‐72. - PubMed
Ramaratnam 2008
Ranganathan 2005
Schoeler 2014
-
- Schoeder NE, Wood S, Aldridge V, Sander JW, Cross JH, Sisodiya SM. Ketogenic dietary therapies for adults with epilepsy: feasibility and classification of response. Epilepsy & Behavior 2014;37:77‐81. - PubMed
Stavem 2000
-
- Stavem K, Kloster R, Rossberg E, Larsson PG, Dahl R, Kinge E, et al. Acupuncture in intractable epilepsy: lack of effect on health‐related quality of life. Seizure 2000;9(6):422‐6. - PubMed
Wiebe 2001
-
- Wiebe S, Blume WT, Girvin JP, Eliasziw M. A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal‐lobe epilepsy. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345(5):311‐8. - PubMed
Zarrelli 1999
-
- Zarrelli MM, Beghi E, Rocca WA, Hauser WA. Incidence of epileptic syndromes in Rochester, Minnesota: 1980‐1984. Epilepsia 1999;40(12):1708‐14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical