Genome analysis of quorum sensing Cedecea neteri SSMD04 leads to identification of its novel signaling synthase (cneI), cognate receptor (cneR) and an orphan receptor
- PMID: 26355540
- PMCID: PMC4562240
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1216
Genome analysis of quorum sensing Cedecea neteri SSMD04 leads to identification of its novel signaling synthase (cneI), cognate receptor (cneR) and an orphan receptor
Abstract
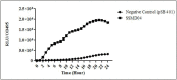
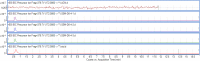
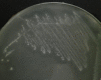
Cedecea neteri is a very rare human pathogen. We have isolated a strain of C. neteri SSMD04 from pickled mackerel sashimi identified using molecular and phenotypics approaches. Using the biosensor Chromobacterium violaceum CV026, we have demonstrated the presence of short chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) type quorum sensing (QS) activity in C. neteri SSMD04. Triple quadrupole LC/MS analysis revealed that C. neteri SSMD04 produced short chain N-butyryl-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL). With the available genome information of C. neteri SSMD04, we went on to analyse and identified a pair of luxI/R homologues in this genome that share the highest similarity with croI/R homologues from Citrobacter rodentium. The AHL synthase, which we named cneI(636 bp), was found in the genome sequences of C. neteri SSMD04. At a distance of 8bp from cneI is a sequence encoding a hypothetical protein, potentially the cognate receptor, a luxR homologue which we named it as cneR. Analysis of this protein amino acid sequence reveals two signature domains, the autoinducer-binding domain and the C-terminal effector which is typical characteristic of luxR. In addition, we found that this genome harboured an orphan luxR that is most closely related to easR in Enterobacter asburiae. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the AHL production activity in C. neteri, and the discovery of its luxI/R homologues, the orphan receptor and its whole genome sequence.
Keywords: Autoinducer; Food microbiology; Mass spectrometry; N-acyl-homoserine lactone; N-butyryl-homoserine lactone; Quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cloning and Characterization of the Autoinducer Synthase Gene from Lipid-Degrading Bacterium Cedecea neteri.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jan 31;8:72. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00072. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28197135 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of quorum sensing LuxR-type transcriptional regulator, EasR in Enterobacter asburiae strain L1.PeerJ. 2020 Oct 21;8:e10068. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10068. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33150063 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of quorum sensing genes and N-acyl homoserine lactones in Citrobacter amalonaticus strain YG6.Gene. 2019 Feb 5;684:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30321658
-
Complete Genome Sequence of Cedecea neteri Strain SSMD04, a Bacterium Isolated from Pickled Mackerel Sashimi.Genome Announc. 2014 Dec 18;2(6):e01339-14. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01339-14. Genome Announc. 2014. PMID: 25523782 Free PMC article.
-
An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00152. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25389523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rare case of urinary tract infection caused by Cedecea lapagei in a 93-year-old patient in southern Italy.Infez Med. 2025 Jun 1;33(2):221-225. doi: 10.53854/liim-3302-8. eCollection 2025. Infez Med. 2025. PMID: 40519341 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and Characterization of the Autoinducer Synthase Gene from Lipid-Degrading Bacterium Cedecea neteri.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jan 31;8:72. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00072. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28197135 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary tract infection by a rare pathogen Cedecea neteri in a pregnant female with Polyhydramnios: rare case report from UAE.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 2;21(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06298-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34215203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aziz RK, Devoid S, Disz T, Edwards RA, Henry CS, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Overbeek R, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Stevens RL, Vonstein V, Xia F. SEED servers: high-performance access to the SEED genomes, annotations, and metabolic models. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e1216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

