Identification of a novel ovine LH-beta promoter region, which dramatically enhances its promoter activity
- PMID: 26355566
- PMCID: PMC4554545
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-015-1182-5
Identification of a novel ovine LH-beta promoter region, which dramatically enhances its promoter activity
Abstract
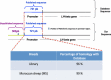
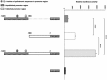
The luteinizing hormone beta subunit (LH-beta) gene plays a critical role in reproduction. In order to characterize and analyze the promoter region of LH-beta in sheep, a genomic library was constructed in phage lambda gt 10 and screened. A novel region of 1,224 bp upstream from the targeted LH-beta gene was identified. Blasting this sequence showed a perfect homology for the first 721 bp sequence with an upstream ovine LH-beta sequence in the database. However, the remaining 5'-503 bp showed no sequence matching. DNA from Moroccan breeds was isolated and the whole region was amplified and confirmed by sequencing. To further confirm the promoter activity of this region, an in vitro analysis using a luciferase assay was carried out. An increase in the promoter activity of the whole region was demonstrated compared to the empty vector. More interestingly, the unpublished region significantly enhanced the promoter activity compared to the known region alone. To predict putative transcription factor binding-sites (TFBSs), an in silico analysis was performed using the TFSEARCH program. The region features many TFBSs and contains two palindrome sequences of 17- and 18-bp. Taken together, a novel region was identified and confirmed in sheep which contained a promoter activity rich with binding sites for a putative regulatory element as shown in silico.
Keywords: LH-beta; Luciferase assay; Promoter; Reproduction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Concerted transcriptional activation of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene by insulin and luteinizing hormone in cultured porcine granulosa-luteal cells: possible convergence of protein kinase a, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Endocrinology. 2001 Jul;142(7):2921-8. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.7.8287. Endocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11416012
-
Identification of a single SNP that affects the promoter activity in the Moroccan prolific D'man breed.J Anim Sci. 2015 May;93(5):2064-73. doi: 10.2527/jas.2014-8669. J Anim Sci. 2015. PMID: 26020302
-
Expression of luteinising hormone-beta subunit chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (LH-beta-CAT) fusion gene in rat pituitary cells: induction by cyclic 3'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP).Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Sep;80(1-3):193-202. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90156-m. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991. PMID: 1659545
-
Novel polymorphisms in UTR and coding region of inducible heat shock protein 70.1 gene in tropically adapted Indian zebu cattle (Bos indicus) and riverine buffalo (Bubalus bubalis).Gene. 2013 Sep 25;527(2):606-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.078. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23792016
-
Structure and regulation of the luteinizing hormone receptor gene.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995 Jun;53(1-6):283-91. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00115-g. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7626469 Review.
References
-
- Blundell R, Felice AE. Detection of new genomic landmarks in the maltese goat using Rapd PCR. J Anim Vet Adv. 2006;5:602–607.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

