High pressure jet injection of viscous solutions for endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD): first clinical experience
- PMID: 26356488
- PMCID: PMC4554496
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1391902
High pressure jet injection of viscous solutions for endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD): first clinical experience
Abstract
Background: Long lasting elevation is a key factor during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and can be obtained by water jet injection of saline solution or by viscous macromolecular solutions. In a previous animal study, we assessed the Nestis Enki II system to combine jet injection and viscous solutions. In the present work, we used this combination in humans in different sites of the digestive tract.
Methods: We retrospectively report all of the consecutive ESD procedures performed with jet injection of viscous solutions in four centers. Information was collected about the lesion, the procedure, the histological result, and the outcomes for the patient.
Results: In total, 45 resections were completed by six operators: five experts and one beginner with only one previous experience in human ESD. Lesions were located in the esophagus (10), the stomach (11), the duodenum (1), the colon (1) and the rectum (22). Average maximal lesion diameter was 4.8 cm (SD 2.4, range 2 - 11 cm), average lesion surface area was 19.8 cm(2) (SD 17.7, range 2.2 - 72 cm(2)), and average duration of procedure was 79.9 min (SD 50.3 min, range 19 - 225 min). ESD could be conducted while the endoscope was retroflexed at its maximum in 26 cases. Four adverse events were observed: two diminutive perforations and two delayed bleeding occurrences treated conservatively. The R0 resection rate was 91.1 %. The catheter was obstructed in six occurrences of bleeding.
Conclusion: Endoscopic submucosal dissection using high pressure injection of viscous macromolecular solutions is safe and effective in different parts of the digestive tract. It does not impede working with the endoscope in the maximal retroflexed position.
Conflict of interest statement
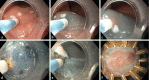
Figures

References
-
- Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N. et al.New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy. 2001;33:221–226. - PubMed
-
- Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N. et al.Endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:688–694. - PubMed
-
- Ciocîrlan M, Pioche M, Lepilliez V. et al.The ENKI-2 water-jet system versus Dual Knife for endoscopic submucosal dissection of colorectal lesions: a randomized comparative animal study. Endoscopy. 2014;46:139–143. - PubMed
-
- Yahagi N, Neuhaus H, Schumacher B. et al.Comparison of standard endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) versus an optimized ESD technique for the colon: an animal study. Endoscopy. 2009;41:340–345. - PubMed
-
- Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Nakamura M. et al.Successful outcomes of a novel endoscopic treatment for GI tumors: endoscopic submucosal dissection with a mixture of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and sugar. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:243–249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

