Novel Axl-driven signaling pathway and molecular signature characterize high-grade ovarian cancer patients with poor clinical outcome
- PMID: 26356564
- PMCID: PMC4741573
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5087
Novel Axl-driven signaling pathway and molecular signature characterize high-grade ovarian cancer patients with poor clinical outcome
Abstract
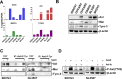
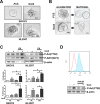
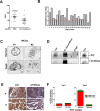
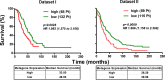
High-grade epithelial ovarian cancer (HGEOC) is a clinically diverse and molecularly heterogeneous disease comprising subtypes with distinct biological features and outcomes. The receptor tyrosine kinases, expressed by EOC cells, and their ligands, present in the microenvironment, activate signaling pathways, which promote EOC cells dissemination. Herein, we established a molecular link between the presence of Gas6 ligand in the ascites of HGEOCs, the expression and activation of its receptor Axl in ovarian cancer cell lines and biopsies, and the progression of these tumors. We demonstrated that Gas6/Axl signalling converges on the integrin β3 pathway in the presence of the adaptor protein p130Cas, thus inducing tumor cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix and invasion. Accordingly, Axl and p130Cas were significantly co-expressed in HGEOC samples. Clinically, we identified an Axl-associated signature of 62 genes able to portray the HGEOCs with the shortest overall survival. These data biologically characterize a group of HGEOCs and could help guide a more effective therapeutic approach to be taken for these patients.
Keywords: Axl; Gas6; extracellular matrix; ovarian cancer; p130Cas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tothill RW, Tinker AV, George J, Brown R, Fox SB, Lade S, Johnson DS, Trivett MK, Etemadmoghadam D, Locandro B, Traficante N, Fereday S, Hung JA, Chiew YE, Haviv I, Gertig D, DeFazio A, Bowtell DD. Novel molecular subtypes of serous and endometrioid ovarian cancer linked to clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5198–5208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

