Comparing Effects of Biologic Agents in Treating Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multiple Treatment Comparison Regression Analysis
- PMID: 26356639
- PMCID: PMC4565694
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137258
Comparing Effects of Biologic Agents in Treating Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multiple Treatment Comparison Regression Analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Comparing Effects of Biologic Agents in Treating Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Multiple Treatment Comparison Regression Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 26;11(1):e0146633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146633. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26812687 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
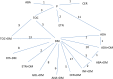
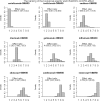
Rheumatoid arthritis patients have been treated with disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and the newer biologic drugs. We sought to compare and rank the biologics with respect to efficacy. We performed a literature search identifying 54 publications encompassing 9 biologics. We conducted a multiple treatment comparison regression analysis letting the number experiencing a 50% improvement on the ACR score be dependent upon dose level and disease duration for assessing the comparable relative effect between biologics and placebo or DMARD. The analysis embraced all treatment and comparator arms over all publications. Hence, all measured effects of any biologic agent contributed to the comparison of all biologic agents relative to each other either given alone or combined with DMARD. We found the drug effect to be dependent on dose level, but not on disease duration, and the impact of a high versus low dose level was the same for all drugs (higher doses indicated a higher frequency of ACR50 scores). The ranking of the drugs when given without DMARD was certolizumab (ranked highest), etanercept, tocilizumab/ abatacept and adalimumab. The ranking of the drugs when given with DMARD was certolizumab (ranked highest), tocilizumab, anakinra/rituximab, golimumab/ infliximab/ abatacept, adalimumab/ etanercept [corrected]. Still, all drugs were effective. All biologic agents were effective compared to placebo, with certolizumab the most effective and adalimumab (without DMARD treatment) and adalimumab/ etanercept (combined with DMARD treatment) the least effective. The drugs were in general more effective, except for etanercept, when given together with DMARDs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Lard LR, Visser H, Spreyer I, et al. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of two cohorts who received different treatment strategies. Am J Med 2001; 111: 446 – 51. - PubMed
-
- Olsen NJ, Stein M. New drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2167 – 79.J Rheumatol Suppl. 2002 Nov; 66:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Emery P. Evidence supporting the benefit of early intervention in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2002. November; 66: 3–8. - PubMed
-
- Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, et al. Update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care & Research May 2012; Vol. 64, No. 5, 625–639. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

