Long-term outcomes of limbal relaxing incisions during cataract surgery: aberrometric analysis
- PMID: 26357459
- PMCID: PMC4560521
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S89024
Long-term outcomes of limbal relaxing incisions during cataract surgery: aberrometric analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the final changes in corneal wavefront aberration by limbal relaxing incisions (LRIs) after cataract surgery.
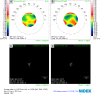
Methods: This prospective cumulative interventional nonrandomized case study included cataract and astigmatic patients undergoing LRIs and phaco with intraocular lens implantation. LRIs were planned using Donnenfeld nomogram. The root mean square of corneal wave aberration for total Z(n,i)(1≤n≤8), astigmatism Z(2,±1), coma Z(3-5-7,±1), trefoil Z(3-5-7,±2), spherical Z(4-6-8,0), and higher-order aberration (HOA) Z(3≤n≤8) was examined before and 3 years after surgery (optical path difference-Scan II [OPD-Scan II)]. Uncorrected distance visual acuity and best-corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) for distance, keratometric cylinder, and variations in average corneal power were also analyzed.
Results: Sixty-four eyes of 48 patients were included in the study. Age ranged from 42 to 92 years (70.6±8.4 years). After LRIs, uncorrected distance visual acuity and best-corrected distance visual acuity improved statistically (P<0.01). The keratometric cylinder value decreased by 40.1%, but analysis of KP90 and KP135 polar values did not show any decrease that could be statistically confirmed (P=0.22 and P=0.24). No significant changes were detected in root mean square of total (P=0.61) and HOAs (P=0.13) aberrations. LRIs did not induce alteration in central corneal power confirming a 1:1 coupling ratio.
Conclusion: LRIs determined a nonsignificant alteration of corneal HOA. Therefore, LRIs can be still considered a qualitatively viable mean in those cases where toric intraocular lenses are contraindicated or not available. Yet, the authors raise the question of nonpersonalized nomograms, as in the present study, LRIs did not reach the preset target cylinder.
Keywords: astigmatism; intraocular lens; ocular wavefront; wavefront aberration.
Figures

References
-
- Nichamin LD. Astigmatism control. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2006;19(4):485–493. - PubMed
-
- Gills JP, Van Der Karr M, Cherchio M. Combined toric intraocular lens implantation and relaxing incisions to reduce high pre-existing astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28:1585–1588. - PubMed
-
- Budak K, Friedman NJ, Koch DD. Limbal relaxing incisions with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998;24:503–508. - PubMed
-
- Müller-Jensen K, Fischer P, Siepe U. Limbal relaxing incisions to correct astigmatism in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 1999;15:586–589. - PubMed
-
- Montés-Micó R, Munoz G, Albarran-Diego C, Rodriguez-Galietero A, Aliò JL. Corneal aberrations after astigmatic keratotomy combined with laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30:1418–1424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

