Norepinephrine induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HT-29 and A549 cells in vitro
- PMID: 26358081
- PMCID: PMC11819271
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-015-2044-9
Norepinephrine induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HT-29 and A549 cells in vitro
Abstract
Purpose: Norepinephrine (NE) has been implicated in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells. However, the underlying mechanism is poorly understood. The goal of this study was to explore the effect of NE on cancer cell EMT and to investigate the potential mechanism.
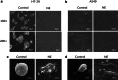
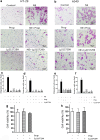
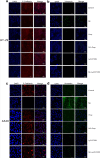
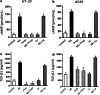
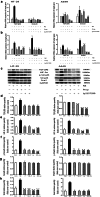
Methods: HT-29 and A549 cells were treated with NE, β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR) antagonist (propranolol) or inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) receptor type I kinase (Ly2157299). Morphology of cells was observed with optical and electron microscope and immunofluorescence staining. Cellular migration and invasion were tested with transwell migration assay and Matrigel invasion assay, respectively. TGF-β1 and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) were quantified. EMT markers and signaling pathway were measured by RT-PCR and western blot.
Results: NE stimulated TGF-β1 secretion and intracellular cAMP synthesis, induced morphological alterations in HT-29 and A549 cells, and enhanced their ability of migration and invasion. EMT markers induction was observed in NE-treated cancer cells. The effect of NE could be inhibited by propranolol or Ly2157299. β-AR/TGF-β1 signaling/p-Smad3/Snail and β-AR/TGF-β1 signaling/HIF-1α/Snail were two signaling pathways.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrated that TGF-β1 signaling pathway was a significant factor of NE-induced cancer cells EMT. The data also suggested that psychological stress might be a risk factor which enhances the ability of migration or invasion of cancer cells.
Keywords: Adrenergic receptor; Chronic stress; Epithelial–mesenchymal transition; Norepinephrine; Transforming growth factor-β1.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that no conflict of interest exists in this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Akhurst RJ, Derynck R (2001) TGF-β signaling in cancer—a double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol 11(11):S44–S51. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(01)02130-4 - PubMed
-
- Barbieri A, Bimonte S, Palma G, Luciano A, Rea D, Giudice A, Scognamiglio G, La Mantia E, Franco R, Perdona S, De Cobelli O, Ferro M, Zappavigna S, Stiuso P, Caraglia M, Arra C (2015) The stress hormone norepinephrine increases migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. doi:10.3892/ijo.2015.3038 - PubMed
-
- Barron TI, Connolly RM, Sharp L, Bennett K, Visvanathan K (2011) Beta blockers and breast cancer mortality: a population-based study. J Clin Oncol 29(19):2635–2644. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.33.5422 - PubMed
-
- Brabletz T, Hlubek F, Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hiendlmeyer E, Jung A, Kirchner T (2005) Invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer: epithelial–mesenchymal transition, mesenchymal–epithelial transition, stem cells and β-catenin. Cells Tissues Organs 179(1–2):56–65. doi:10.1159/000084509 - PubMed
-
- Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S, Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Cespedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung P, Zhang XH, Byrom D, Riera A, Rossell D, Mangues R, Massague J, Sancho E, Batlle E (2012) Dependency of colorectal cancer on a TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation. Cancer Cell 22(5):571–584. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.013 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

