Acceleration of atherogenesis in ApoE-/- mice exposed to acute or low-dose-rate ionizing radiation
- PMID: 26359350
- PMCID: PMC4741603
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5075
Acceleration of atherogenesis in ApoE-/- mice exposed to acute or low-dose-rate ionizing radiation
Abstract
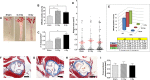
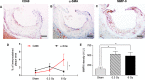
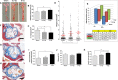
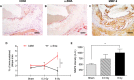
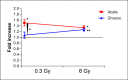
There is epidemiological evidence for increased non-cancer mortality, primarily due to circulatory diseases after radiation exposure above 0.5 Sv. We evaluated the effects of chronic low-dose rate versus acute exposures in a murine model of spontaneous atherogenesis. Female ApoE-/- mice (60 days) were chronically irradiated for 300 days with gamma rays at two different dose rates (1 mGy/day; 20 mGy/day), with total accumulated doses of 0.3 or 6 Gy. For comparison, age-matched ApoE-/- females were acutely exposed to the same doses and sacrificed 300 days post-irradiation. Mice acutely exposed to 0.3 or 6 Gy showed increased atherogenesis compared to age-matched controls, and this effect was persistent. When the same doses were delivered at low dose rate over 300 days, we again observed a significant impact on global development of atherosclerosis, although at 0.3 Gy effects were limited to the descending thoracic aorta. Our data suggest that a moderate dose of 0.3 Gy can have persistent detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, and that a high dose of 6 Gy poses high risks at both high and low dose rates. Our results were clearly nonlinear with dose, suggesting that lower doses may be more damaging than predicted by a linear dose response.
Keywords: ApoE mice; aorta; atherosclerosis; radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
No, there is no conflict of interest that I should disclose, having read the above statement.
Figures
References
-
- Adams MJ, Hardenbergh PH, Constine LS, Lipshultz SE. Radiation-associated cardiovascular disease. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2003;45:55–75. - PubMed
-
- Annals of the ICRP. Early and late effects of radiation in normal tissues and organs: threshold doses for tissue reactions and other non-cancer effects of radiation in a radiation protection context. 2012 public draft. http://www.icrp.org published at ICRP website. - PubMed
-
- Schultz-Hector S, Trott KR. Radiation-induced cardiovascular diseases: is the epidemiologic evidence compatible with the radiobiologic data? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67:10–18. - PubMed
-
- Hendry JH, Akahoshi M, Wang LS, Lipshultz SE, Stewart FA, Trott KR. Radiation-induced cardiovascular injury. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2008;47:189–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

