Respiratory and allergic health effects in a young population in proximity of a major industrial park in Oman
- PMID: 26359504
- PMCID: PMC4752616
- DOI: 10.1136/jech-2015-205609
Respiratory and allergic health effects in a young population in proximity of a major industrial park in Oman
Abstract
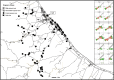
Background: Sohar industrial zone (SIZ), Oman, which started operating in 2006, contains many industries that potentially affect the health of the local population. This study's aim was to evaluate the health effects in a young population living near SIZ.
Methods: Patient visits to state health clinics for acute respiratory diseases (ARD), asthma, conjunctivitis and dermatitis were obtained for the period of 2006 to 2010, for children ages <20 years old, for two large provinces around SIZ. Three exposure zones were defined on the basis of the distance from SIZ determined as: ≤5, >5 to 10, ≥20 km to represent high, intermediate and control exposure zones, respectively. Age-specific and gender-specific monthly counts of visits were modelled using generalised additive models controlling for time trends. The high and intermediate exposure zones were later combined together due to the similarity of associations. Exposure effect modification by age, gender and socioeconomic status (SES) was also tested.
Results: Living within 10 km from SIZ showed a greater association with ARD (risk ratio (RR)=2.5; 95% CI=2.3 to 2.7), asthma (RR=3.7; 95% CI=3.1 to 4.5), conjunctivitis (RR=3.1; 95% CI=2.9 to 3.5) and dermatitis (RR=2.7; 95% CI=2.5 to 3.0) when compared with the control zone. No differences in associations were found for gender and SES groups; greater effects were noticed in the ≤14-year-old group for asthma.
Conclusions: This is the first study conducted in Oman to examine the health effects of a young population living near an industrial park. We hope that these findings will contribute in future developments of environmental health policies in Oman.
Keywords: ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH; Environmental epidemiology; PRIMARY HEALTH CARE; PUBLIC HEALTH; RESPIRATORY DI.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
References
-
- Schwartz J. Air pollution and children's health. Pediatrics 2004;113:1037–43. - PubMed
-
- Prüss-Üstün A, Corvalán C. Preventing disease through healthy environments. World Health Organization, 2006. (cited Apr 2014) http://www.who.int/entity/quantifying_ehimpacts/publications/preventingd...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
