Brain Metastases at Presentation in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26359696
- PMCID: PMC4833709
- DOI: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000230
Brain Metastases at Presentation in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Objective: We used brain radiotherapy as a surrogate for the presence of brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) to determine the prevalence of brain metastases using the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results database.
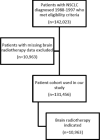
Methods: Patients with NSCLC diagnosed between 1988 and 1997 were subdivided according to brain radiotherapy status at presentation into: "none" or "radiation therapy indicated." We calculated the frequency of brain radiotherapy use in all patients. Odds ratios (ORs) for the indication of brain radiotherapy were calculated for individual prespecified covariates of interest. All statistical tests were 2-sided and P<0.05 were considered significant.
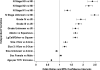
Results: At presentation, brain radiotherapy was indicated in 10,963 (8.3%) of the 131,456 patients diagnosed with NSCLC between 1988 and 1997. On multivariable analysis the following were significantly associated with brain radiotherapy use: age (OR, 0.653 per 10 y increase in age; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.642, 0.665); female sex (OR, 1.05; 95% CI: 1.01, 1.10]); adenocarcinoma histology (HR, 1.67; 95% CI: 1.58, 1.76) or large cell or other histology (OR, 1.67; 95% CI: 1.57, 1.77); tumor size>3 cm (3.1 to 5 cm OR, 1.22; 95% CI: 1.14, 1.30 and >5 cm OR, 1.25; 95% CI: 1.17, 1.33); tumor grade >II (grade III OR, 1.82; 95% CI: 1.69, 1.95 and grade IV OR, 1.91; 95% CI: 1.73, 2.11); and nodal involvement N1 (OR, 1.33; 95% CI: 1.20, 1.47), N2 (OR, 2.24; 95% CI: 2.10, 2.40), and N3 (OR, 2.39; 95% CI: 2.19, 2.60).
Conclusions: Brain radiotherapy is indicated in over 8% of patients with NSCLC at presentation. We demonstrated that the risk of brain metastasis at presentation may be stratified with the use of 6 clinical factors.
Figures


Comment in
-
The risk factors for brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Nov;6(Suppl 1):S66. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.10.27. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30613641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21166. - PubMed
-
- Patel RR, Mehta MP. Targeted therapy for brain metastases: improving the therapeutic ratio. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1675–1683. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2489. - PubMed
-
- Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, Posner JB. Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol. 1988;45:741–744. - PubMed
-
- Schouten LJ, Rutten J, Huveneers HA, Twijnstra A. Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. Cancer. 2002;94:2698–2705. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

