Non-genomic and Immune Evolution of Melanoma Acquiring MAPKi Resistance
- PMID: 26359985
- PMCID: PMC4821508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.061
Non-genomic and Immune Evolution of Melanoma Acquiring MAPKi Resistance
Abstract
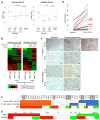
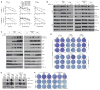
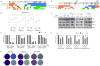
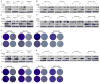
Clinically acquired resistance to MAPK inhibitor (MAPKi) therapies for melanoma cannot be fully explained by genomic mechanisms and may be accompanied by co-evolution of intra-tumoral immunity. We sought to discover non-genomic mechanisms of acquired resistance and dynamic immune compositions by a comparative, transcriptomic-methylomic analysis of patient-matched melanoma tumors biopsied before therapy and during disease progression. Transcriptomic alterations across resistant tumors were highly recurrent, in contrast to mutations, and were frequently correlated with differential methylation of tumor cell-intrinsic CpG sites. We identified in the tumor cell compartment supra-physiologic c-MET up-expression, infra-physiologic LEF1 down-expression and YAP1 signature enrichment as drivers of acquired resistance. Importantly, high intra-tumoral cytolytic T cell inflammation prior to MAPKi therapy preceded CD8 T cell deficiency/exhaustion and loss of antigen presentation in half of disease-progressive melanomas, suggesting cross-resistance to salvage anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. Thus, melanoma acquires MAPKi resistance with highly dynamic and recurrent non-genomic alterations and co-evolving intra-tumoral immunity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Beyond Genomics: Multidimensional Analysis of Cancer Therapy Resistance.Trends Immunol. 2015 Nov;36(11):665-667. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.09.003. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26440701 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic resistance: Multiple mechanisms to keep going.Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 Nov;15(11):635. doi: 10.1038/nrc4034. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26493640 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferrari de Andrade L, Ngiow SF, Stannard K, Rusakiewicz S, Kalimutho M, Khanna KK, Tey SK, Takeda K, Zitvogel L, Martinet L, et al. Natural Killer Cells Are Essential for the Ability of BRAF Inhibitors to Control BRAFV600E-Mutant Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2014;74:7298–7308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

