The new psychoactive substances 5-(2-aminopropyl)indole (5-IT) and 6-(2-aminopropyl)indole (6-IT) interact with monoamine transporters in brain tissue
- PMID: 26362361
- PMCID: PMC4681602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.004
The new psychoactive substances 5-(2-aminopropyl)indole (5-IT) and 6-(2-aminopropyl)indole (6-IT) interact with monoamine transporters in brain tissue
Abstract
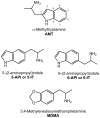
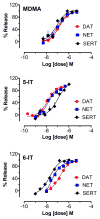
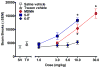
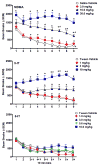
In recent years, use of psychoactive synthetic stimulants has grown rapidly. 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole (5-IT) is a synthetic drug associated with a number of fatalities, that appears to be one of the newest 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) replacements. Here, the monoamine-releasing properties of 5-IT, its structural isomer 6-(2-aminopropyl)indole (6-IT), and MDMA were compared using in vitro release assays at transporters for dopamine (DAT), norepinephrine (NET), and serotonin (SERT) in rat brain synaptosomes. In vivo pharmacology was assessed by locomotor activity and a functional observational battery (FOB) in mice. 5-IT and 6-IT were potent substrates at DAT, NET, and SERT. In contrast with the non-selective releasing properties of MDMA, 5-IT displayed greater potency for release at DAT over SERT, while 6-IT displayed greater potency for release at SERT over DAT. 5-IT produced locomotor stimulation and typical stimulant effects in the FOB similar to those produced by MDMA. Conversely, 6-IT increased behaviors associated with 5-HT toxicity. 5-IT likely has high abuse potential, which may be somewhat diminished by its slow onset of in vivo effects, whereas 6-IT may have low abuse liability, but enhanced risk for adverse effects. Results indicate that subtle differences in the chemical structure of transporter ligands can have profound effects on biological activity. The potent monoamine-releasing actions of 5-IT, coupled with its known inhibition of MAO A, could underlie its dangerous effects when administered alone, and in combination with other monoaminergic drugs or medications. Consequently, 5-IT and related compounds may pose substantial risk for abuse and serious adverse effects in human users.
Keywords: 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA); 5-(2-Aminopropyl)indole (5-IT); 6-(2-Aminopropyl)indole (6-IT); Locomotor activity; Monoamine releaser; Synthetic stimulants.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aarde SM, Angrish D, Barlow DJ, Wright MJ, Jr, Vandewater SA, Creehan KM, Houseknecht KL, Dickerson TJ, Taffe MA. Mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone) supports intravenous self-administration in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats. Addict Biol. 2013a;18:786–799. doi: 10.1111/adb.12038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aarde SM, Huang PK, Creehan KM, Dickerson TJ, Taffe MA. The novel recreational drug 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) is a potent psychomotor stimulant: self-administration and locomotor activity in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2013b;71:130–140. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aarde SM, Creehan KM, Vandewater SA, Dickerson TJ, Taffe MA. In vivo potency and efficacy of the novel cathinone α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone and 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone: self-administration and locomotor stimulation in male rats. Psychopharmacology. 2015 doi: 10.1007/s00213-00015-03944-00218. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abreu ME, Bigelow GE, Fleisher L, Walsh SL. Effect of intravenous injection speed on responses to cocaine and hydromorphone in humans. Psychopharmacology. 2001;154:76–84. - PubMed
-
- Bäckberg M, Beck O, Hultén P, Rosengren-Holmberg J, Helander A. Intoxications of the new psychoactive substance 5-(2-aminopropyl)indole (5-IT): a case series from the Swedish STRIDA project. Clin Toxicol. 2014;52:6618–6624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

