A pilot study on the use of acupuncture or pelvic floor muscle training for mixed urinary incontinence
- PMID: 26362793
- PMCID: PMC4789711
- DOI: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010828
A pilot study on the use of acupuncture or pelvic floor muscle training for mixed urinary incontinence
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the feasibility and acceptability of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) acupuncture and pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) in reducing symptoms and bothersomeness in women with mixed urinary incontinence (MUI); and to estimate the sample size for a full scale trial.
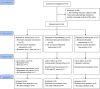
Methods: Thirty-four women with MUI were randomly assigned to either 12 sessions of TCM acupuncture, 12 sessions of PFMT, or to a waiting list control group. Outcome measures included an assessment of interest to participate in the trial, identification of successful recruitment strategies, the appropriateness of eligibility criteria, and compliance with treatment. Clinical outcomes were assessed at baseline and 12 weeks, and included the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Urinary Incontinence-Short Form (ICIQ-UI SF), expectations of treatment effect, and adverse events.
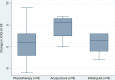
Results: Recruitment was feasible and randomisation worked adequately by means of SurveyMonkey. SurveyMonkey does not permit stratification by ICIQ-UI SF baseline score. Fourteen of 22 women found the treatment options acceptable. The dropout rate was high, especially in the control group (6/12). Outcome forms were completed by 20 of 34 women. The median (IQR) changes of the ICIQ-UI SF scores in the acupuncture, physiotherapy, and waiting list group were 5.5 (2.3 to 6.8), 1.0 (-3.0 to 4.5), and 1.5 (-1.5 to 3.0), respectively, suggesting the need for a full scale trial.
Conclusions: Women with MUI were willing to participate in this study. There is a need for adjusting eligibility criteria. A sample size of 129 women, 43 in three arms, is required. No major adverse events occurred.
Keywords: ACUPUNCTURE; PHYSIOTHERAPY; UROLOGY.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

References
-
- Haylen BT, De Ridder D, Freeman RM, et al. . An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn 2010;29:4–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

