Novel Insights into Interleukin 6 (IL-6) Cis- and Trans-signaling Pathways by Differentially Manipulating the Assembly of the IL-6 Signaling Complex
- PMID: 26363066
- PMCID: PMC4646397
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.682138
Novel Insights into Interleukin 6 (IL-6) Cis- and Trans-signaling Pathways by Differentially Manipulating the Assembly of the IL-6 Signaling Complex
Abstract
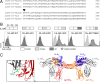
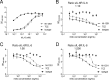
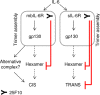
The IL-6 signaling complex is described as a hexamer, formed by the association of two IL-6·IL-6 receptor (IL-6R)·gp130 trimers, with gp130 being the signal transducer inducing cis- and trans-mediated signaling via a membrane-bound or soluble form of the IL-6R, respectively. 25F10 is an anti-mouse IL-6R mAb that binds to both membrane-bound IL-6R and soluble IL-6R with the unique property of specifically inhibiting trans-mediated signaling events. In this study, epitope mapping revealed that 25F10 interacts at site IIb of IL-6R but allows the binding of IL-6 to the IL-6R and the recruitment of gp130, forming a trimer complex. Binding of 25F10 to IL-6R prevented the formation of the hexameric complex obligate for trans-mediated signaling, suggesting that the cis- and trans-modes of IL-6 signaling adopt different mechanisms for receptor complex assembly. To study this phenomenon also in the human system, we developed NI-1201, a mAb that targets, in the human IL-6R sequence, the epitope recognized by 25F10 for mice. Interestingly, NI-1201, however, did not selectively inhibit human IL-6 trans-signaling, although both mAbs produced beneficial outcomes in conditions of exacerbated IL-6 as compared with a site I-directed mAb. These findings shed light on the complexity of IL-6 signaling. First, triggering cis- versus trans-mediated IL-6 signaling occurs via distinctive mechanisms for receptor complex assembly in mice. Second, the formation of the receptor complex leading to cis- and trans-signaling biology in mice and humans is different, and this should be taken into account when developing strategies to inhibit IL-6 clinically.
Keywords: antibody; complex; interleukin 6 (IL-6); receptor; signaling.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Mihara M., Hashizume M., Yoshida H., Suzuki M., and Shiina M. (2012) IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin. Sci. 122, 143–159 - PubMed
-
- Peters M., Müller A. M., and Rose-John S. (1998) Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptor: direct stimulation of gp130 and hematopoiesis. Blood 92, 3495–3504 - PubMed
-
- Scheller J., Chalaris A., Schmidt-Arras D., and Rose-John S. (2011) The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813, 878–888 - PubMed
-
- Scheller J., Garbers C., and Rose-John S. (2014) Interleukin-6: from basic biology to selective blockade of pro-inflammatory activities. Semin. Immunol. 26, 2–12 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

