Agonism, Antagonism, and Inverse Agonism Bias at the Ghrelin Receptor Signaling
- PMID: 26363071
- PMCID: PMC4646384
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.659250
Agonism, Antagonism, and Inverse Agonism Bias at the Ghrelin Receptor Signaling
Abstract
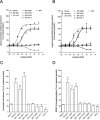
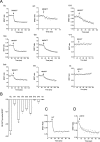
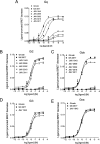
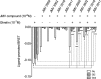
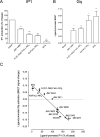
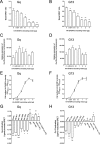
The G protein-coupled receptor GHS-R1a mediates ghrelin-induced growth hormone secretion, food intake, and reward-seeking behaviors. GHS-R1a signals through Gq, Gi/o, G13, and arrestin. Biasing GHS-R1a signaling with specific ligands may lead to the development of more selective drugs to treat obesity or addiction with minimal side effects. To delineate ligand selectivity at GHS-R1a signaling, we analyzed in detail the efficacy of a panel of synthetic ligands activating the different pathways associated with GHS-R1a in HEK293T cells. Besides β-arrestin2 recruitment and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, we monitored activation of a large panel of G protein subtypes using a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based assay with G protein-activation biosensors. We first found that unlike full agonists, Gq partial agonists were unable to trigger β-arrestin2 recruitment and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Using G protein-activation biosensors, we then demonstrated that ghrelin promoted activation of Gq, Gi1, Gi2, Gi3, Goa, Gob, and G13 but not Gs and G12. Besides, we identified some GHS-R1a ligands that preferentially activated Gq and antagonized ghrelin-mediated Gi/Go activation. Finally, we unambiguously demonstrated that in addition to Gq, GHS-R1a also promoted constitutive activation of G13. Importantly, we identified some ligands that were selective inverse agonists toward Gq but not of G13. This demonstrates that bias at GHS-R1a signaling can occur not only with regard to agonism but also to inverse agonism. Our data, combined with other in vivo studies, may facilitate the design of drugs selectively targeting individual signaling pathways to treat only the therapeutically relevant function.
Keywords: G protein; G protein subtypes; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET); cell signaling; ghrelin; hormone receptor; signaling bias.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Modification of ghrelin receptor signaling by somatostatin receptor-5 regulates insulin release.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 13;109(46):19003-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209590109. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23112170 Free PMC article.
-
Biased signaling regulates the pleiotropic effects of the urotensin II receptor to modulate its cellular behaviors.FASEB J. 2014 Dec;28(12):5148-62. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-249771. Epub 2014 Sep 2. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 25183668
-
High constitutive activity is an intrinsic feature of ghrelin receptor protein: a study with a functional monomeric GHS-R1a receptor reconstituted in lipid discs.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 3;287(6):3630-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.288324. Epub 2011 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22117076 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Development of Nonpeptide Small Molecules Targeting Ghrelin Receptor.J Med Chem. 2022 Feb 24;65(4):3098-3118. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c02191. Epub 2022 Feb 14. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35157454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ghrelin receptor (GHS-R1A) agonists show potential as interventive agents during aging.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1119:147-64. doi: 10.1196/annals.1404.023. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056963 Review.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin Receptor Antagonism of Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference and Intravenous Self-Administration in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 26;19(10):2925. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102925. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30261633 Free PMC article.
-
A role for leptin and ghrelin in the augmentation of heroin seeking induced by chronic food restriction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Mar;237(3):787-800. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05415-9. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31811350
-
The five dimensions of receptor pharmacology exemplified by melatonin receptors: An opinion.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019 Dec 29;8(1):e00556. doi: 10.1002/prp2.556. eCollection 2020 Feb. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019. PMID: 31893125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a Cell Line Stably Expressing the Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor to Identify Crocin as a Ghrelin Agonist.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 5;12(12):1813. doi: 10.3390/biom12121813. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551241 Free PMC article.
-
Quinolones Modulate Ghrelin Receptor Signaling: Potential for a Novel Small Molecule Scaffold in the Treatment of Cachexia.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 30;19(6):1605. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061605. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29848961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kojima M., Hosoda H., Date Y., Nakazato M., Matsuo H., and Kangawa K. (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402, 656–660 - PubMed
-
- Akamizu T., and Kangawa K. (2012) The physiological significance and potential clinical applications of ghrelin. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 23, 197–202 - PubMed
-
- Lagerström M. C., and Schiöth H. B. (2008) Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7, 339–357 - PubMed
-
- Cruz C. R., and Smith R. G. (2008) The growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Vitamins Hormones 77, 47–88 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

