The role of CYP2A5 in liver injury and fibrosis: chemical-specific difference
- PMID: 26363552
- PMCID: PMC4703559
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-015-1172-8
The role of CYP2A5 in liver injury and fibrosis: chemical-specific difference
Abstract
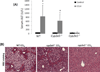
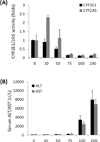
Liver injuries induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCL4) or thioacetamide (TAA) are dependent on cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1). CYP2A5 can be induced by TAA but not by CCL4. In this study, liver injury including fibrosis induced by CCL4 or TAA were investigated in wild-type (WT) mice and CYP2A5 knockout (cyp2a5 (-/-) ) mice as well as in CYP2E1 knockout (cyp2e1 (-/-) ) mice as a comparison. Acute and subchronic liver injuries including fibrosis were induced by CCL4 and TAA in WT mice but not in cyp2e1 (-/-) mice, confirming the indispensable role of CYP2E1 in CCL4 and TAA hepatotoxicity. WT mice and cyp2a5 (-/-) mice developed comparable acute liver injury induced by a single injection of CCL4 as well as subchronic liver injury including fibrosis induced by 1 month of repeated administration of CCL4, suggesting that CYP2A5 does not affect CCL4-induced liver injury and fibrosis. However, while 200 mg/kg TAA-induced acute liver injury was comparable in WT mice and cyp2a5 (-/-) mice, 75 and 100 mg/kg TAA-induced liver injury were more severe in cyp2a5 (-/-) mice than those found in WT mice. After multiple injections with 200 mg/kg TAA for 1 month, while subchronic liver injury as indicated by serum aminotransferases was comparable in WT mice and cyp2a5 (-/-) mice, liver fibrosis was more severe in cyp2a5 (-/-) mice than that found in WT mice. These results suggest that while both CCL4- and TAA-induced liver injuries and fibrosis are CYP2E1 dependent, under some conditions, CYP2A5 may protect against TAA-induced liver injury and fibrosis, but it does not affect CCL4 hepatotoxicity.
Keywords: Cytochrome P450; Fibrosis; Hepatic stellate cell; Liver injury; Metabolism; Oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Abu-Bakar A, Satarug S, Marks GC, Lang MA, Moore MR. Acute cadmium chloride administration induces hepatic and renal CYP2A5 mRNA, protein and activity in the mouse: involvement of transcription factor NRF2. Toxicol Lett. 2004;148:199–210. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Bakar A, Hakkola J, Juvonen R, Rahnasto-Rilla M, Raunio H, Lang MA. Function and regulation of the Cyp2a5/CYP2A6 genes in response to toxic insults in the liver. Curr. Drug Metab. 2013;14:137–150. - PubMed
-
- Avasarala S, Yang L, Sun Y, Leung AW, Chan WY, Cheung WT, Lee SS. A temporal study on the histopathological, biochemical and molecular responses of CCl(4)-induced hepatotoxicity in Cyp2e1-null mice. Toxicology. 2006;228:310–322. - PubMed
-
- Brattin WJ, Glende EA, Jr, Recknagel RO. Pathological mechanisms in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. J Free Radic Biol Med. 1985;1:27–38. - PubMed
-
- Cederbaum A. Nrf2 and antioxidant defense against CYP2E1 toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009;5:1223–1244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

