Identification of Happyhour/MAP4K as Alternative Hpo/Mst-like Kinases in the Hippo Kinase Cascade
- PMID: 26364751
- PMCID: PMC4589524
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.08.014
Identification of Happyhour/MAP4K as Alternative Hpo/Mst-like Kinases in the Hippo Kinase Cascade
Abstract
In Drosophila and mammals, the canonical Hippo kinase cascade is mediated by Hpo/Mst acting through the intermediary kinase Wts/Lats to phosphorylate the transcriptional coactivator Yki/YAP/TAZ. Despite recent reports linking Yki/YAP/TAZ activity to the actin cytoskeleton, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood and/or controversial. Using Drosophila imaginal discs as an in vivo model, we show that Wts, but not Hpo, is genetically indispensable for cytoskeleton-mediated subcellular localization of Yki. Through a systematic screen, we identify the Ste-20 kinase Happyhour (Hppy) and its mammalian counterpart MAP4K1/2/3/5 as an alternative kinase that phosphorylates the hydrophobic motif of Wts/Lats in a similar manner as Hpo/Mst. Consistent with their redundant function as activating kinases of Wts/Lats, combined loss of Hpo/Mst and Hppy/MAP4K abolishes cytoskeleton-mediated regulation of Yki/YAP subcellular localization, as well as YAP cytoplasmic translocation induced by contact inhibition. These Hpo/Mst-like kinases provide an expanded view of the Hippo kinase cascade in development and physiology.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
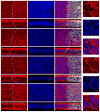



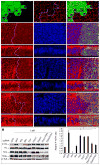


References
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, Piccolo S. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell. 2013;154:1047–1059. - PubMed
-
- Barry ER, Camargo FD. The Hippo superhighway: signaling crossroads converging on the Hippo/Yap pathway in stem cells and development. Current opinion in cell biology. 2013;25:247–253. - PubMed
-
- Bryk B, Hahn K, Cohen SM, Teleman AA. MAP4K3 regulates body size and metabolism in Drosophila. Developmental biology. 2010;344:150–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

