A Review of Epigenetic Markers of Tobacco and Alcohol Consumption
- PMID: 26365064
- PMCID: PMC5040328
- DOI: 10.1002/bsl.2202
A Review of Epigenetic Markers of Tobacco and Alcohol Consumption
Abstract
Over the past two decades, advances in genetic technologies have posed unexpected challenges to the ethical and legal framework guiding the application of the most recent advances in healthcare technologies. By and large, these challenges have been successfully met by the introduction by statutes such as the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA). However, over the past several years, these advances in the ability to measure genetic (or heritable) contributions to medical illness have been joined by advances in epigenetic (or acquired) contributions to common medical illnesses. Unfortunately, the moral and legal framework for the use of these epigenetic technologies, which can objectively determine the presence of medical illnesses such as diabetes or the consumption of substances of abuse, is not as well developed. This communication provides an introduction to the fundamentals of epigenetics and then reviews how some of the latest advances in this technology can now be used to assess the consumption of alcohol and tobacco. Next, the possible mechanisms through which these tools could be employed clinically are discussed. Finally, the authors outline the potential for misuse of this technology and suggest that well-informed policy could play a critical role in shaping the optimal implementation of epigenetic technologies.
Copyright © 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
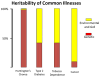




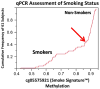
References
-
- Athyros VG, Katsiki N, Doumas M, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP. Effect of tobacco smoking and smoking cessation on plasma lipoproteins and associated major cardiovascular risk factors: A narrative review. Current Medical Research and Opinion. 2013;29(10):1263–1274. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.827566. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

