P16INK4a Upregulation Mediated by SIX6 Defines Retinal Ganglion Cell Pathogenesis in Glaucoma
- PMID: 26365380
- PMCID: PMC4648709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.027
P16INK4a Upregulation Mediated by SIX6 Defines Retinal Ganglion Cell Pathogenesis in Glaucoma
Abstract
Glaucoma, a blinding neurodegenerative disease, whose risk factors include elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), age, and genetics, is characterized by accelerated and progressive retinal ganglion cell (RGC) death. Despite decades of research, the mechanism of RGC death in glaucoma is still unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the genetic effect of the SIX6 risk variant (rs33912345, His141Asn) is enhanced by another major POAG risk gene, p16INK4a (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, isoform INK4a). We further show that the upregulation of homozygous SIX6 risk alleles (CC) leads to an increase in p16INK4a expression, with subsequent cellular senescence, as evidenced in a mouse model of elevated IOP and in human POAG eyes. Our data indicate that SIX6 and/or IOP promotes POAG by directly increasing p16INK4a expression, leading to RGC senescence in adult human retinas. Our study provides important insights linking genetic susceptibility to the underlying mechanism of RGC death and provides a unified theory of glaucoma pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

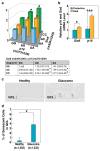
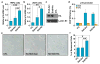



Comment in
-
Blindness: Assassins of eyesight.Nature. 2015 Nov 26;527(7579):456-7. doi: 10.1038/527456a. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26607542 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aldahmesh MA, Khan AO, Hijazi H, Alkuraya FS. Homozygous truncation of SIX6 causes complex microphthalmia in humans. Clinical genetics. 2013;84:198–199. - PubMed
-
- Burdon KP, Macgregor S, Hewitt AW, Sharma S, Chidlow G, Mills RA, Danoy P, Casson R, Viswanathan AC, Liu JZ, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility loci for open angle glaucoma at TMCO1 and CDKN2B-AS1. Nature genetics. 2011;43:574–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HD072754/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD082567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014448/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY022589/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014428/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY023704/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001898/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01HG008135/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044838/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30EY022589/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071872/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018660/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

