Is chest X-ray screening for lung cancer in smokers cost-effective? Evidence from a population-based study in Italy
- PMID: 26366122
- PMCID: PMC4567810
- DOI: 10.1186/s12962-015-0041-0
Is chest X-ray screening for lung cancer in smokers cost-effective? Evidence from a population-based study in Italy
Abstract
Background: After implementation of the PREDICA annual chest X-ray (CXR) screening program in smokers in the general practice setting of Varese-Italy a significant reduction in lung cancer-specific mortality (18 %) was observed. The objective of this study covering July 1997 through December 2006 was to estimate the cost-effectiveness of this intervention.
Methods: We examined detailed information on lung cancer (LC) cases that occurred among smokers invited to be screened in the PREDICA study (Invitation-to-screening Group, n = 5815 subjects) to estimate costs and quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) from LC diagnosis until death. The control group consisted of 156 screening-eligible smokers from the same area, uninvited and unscreened, who developed LC and were treated by usual care. We calculated the incremental net monetary benefit (INMB) by comparing LC management in screening participants (n = 1244 subjects) and in the Invitation-to-screening group versus control group.
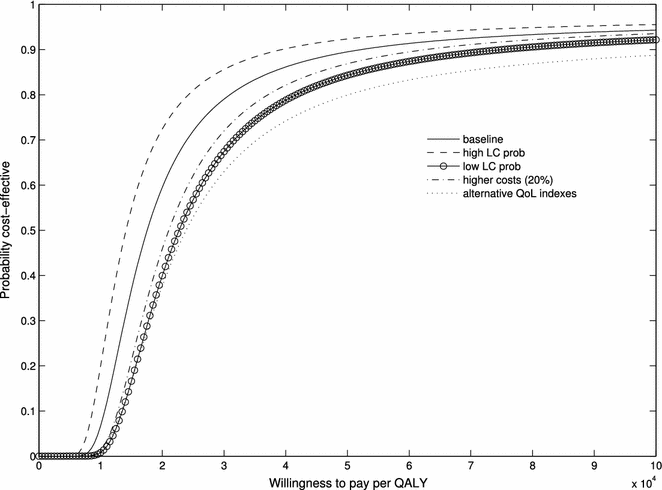
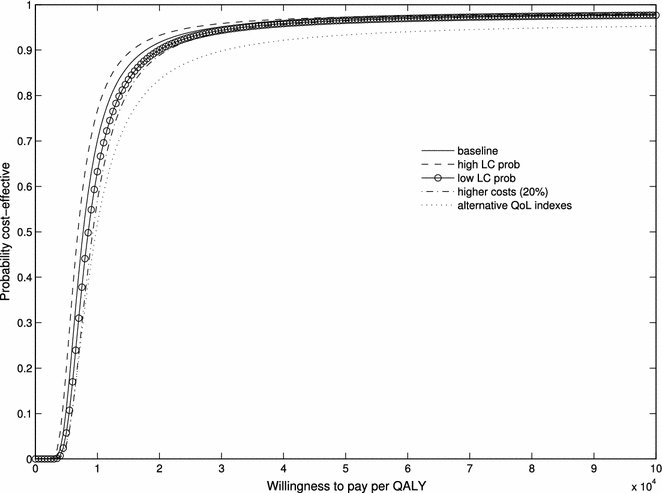
Results: The average number of QALYs since LC diagnosis was 1.7, 1.49 and 1.07, respectively, in screening participants, the invitation-to-screening group, and the control group. The average total cost (screening + management) per LC case was higher in screening participants (€17,516) and the Invitation-to-screening Group (€16,167) than in the control group (€15,503). Assuming a maximum willingness to pay of €30,000/QALY, we found that the intervention was cost-effective with high probability: 79 % for screening participation (screening participants vs. control group) and 95 % for invitation-to-screening (invitation-to-screening group vs. control group).
Conclusions: Based on the PREDICA study, annual CXR screening of high-risk smokers in a general practice setting has high probability of being cost-effective with a maximum willingness to pay of €30,000/QALY.
Keywords: Chest X-ray screening; Cost-effectiveness; Cost-utility; Lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost of a population-based programme of chest x-ray screening for lung cancer.Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2013 Jun;79(2):67-72. doi: 10.4081/monaldi.2013.94. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2013. PMID: 24354094
-
Assessment of lung cancer mortality reduction after chest X-ray screening in smokers: a population-based cohort study in Varese, Italy.Lung Cancer. 2013 Apr;80(1):50-4. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.12.014. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23294502
-
A population-based cohort study of chest x-ray screening in smokers: lung cancer detection findings and follow-up.BMC Cancer. 2012 Jan 17;12:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-18. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22251777 Free PMC article.
-
Lung cancer screening in cigarette smokers in the province of Varese, Italy.Cancer. 2000 Dec 1;89(11 Suppl):2345-8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20001201)89:11+<2345::aid-cncr5>3.3.co;2-2. Cancer. 2000. PMID: 11147609
-
The cost-effectiveness of screening for oral cancer in primary care.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Apr;10(14):1-144, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10140. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16707071 Review.
Cited by
-
P16INK4a gene promoter methylation as a biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer: An updated meta-analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):1032-1040. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12783. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29927090 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of value of biomarkers in diagnosing lung cancer: An overview of systematic reviews protocol.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(19):e15525. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015525. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31083197 Free PMC article.
-
Irish general practitioner (GP) perspectives on impact of direct access radiology on patient care in the community: results from a mixed-methods study.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Feb;193(1):425-434. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03419-1. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37354242 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to Monitoring Guidelines of Amiodarone Adverse Reactions.Health Serv Res Manag Epidemiol. 2019 Apr 16;6:2333392819844635. doi: 10.1177/2333392819844635. eCollection 2019 Jan-Dec. Health Serv Res Manag Epidemiol. 2019. PMID: 31024983 Free PMC article.
-
The Economic Burden of Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Pharmacoecon Open. 2018 Jun;2(2):125-139. doi: 10.1007/s41669-017-0045-0. Pharmacoecon Open. 2018. PMID: 29623624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

