Forecasting individual breast cancer risk using plasma metabolomics and biocontours
- PMID: 26366139
- PMCID: PMC4559100
- DOI: 10.1007/s11306-015-0793-8
Forecasting individual breast cancer risk using plasma metabolomics and biocontours
Abstract
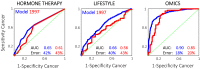
Breast cancer is a major cause of death for women. To improve treatment, current oncology research focuses on discovering and validating new biomarkers for early detection of cancer; so far with limited success. Metabolic profiling of plasma samples and auxiliary lifestyle information was combined by chemometric data fusion. It was possible to create a biocontour, which we define as a complex pattern of relevant biological and phenotypic information. While single markers or known risk factors have close to no predictive value, the developed biocontour provides a forecast which, several years before diagnosis, is on par with how well most current biomarkers can diagnose current cancer. Hence, while e.g. mammography can diagnose current cancer with a sensitivity and specificity of around 75 %, the currently developed biocontour can predict that there is an increased risk that breast cancer will develop in a subject 2-5 years after the sample is taken with sensitivity and specificity well above 80 %. The model was built on data obtained in 1993-1996 and tested on persons sampled a year later in 1997. Metabolic forecasting of cancer by biocontours opens new possibilities for early prediction of individual cancer risk and thus for efficient screening. This may provide new avenues for research into disease mechanisms.
Keywords: Cancer and health cohort; Chemometrics; Danish diet; Early detection; Metabolomics; Multivariate analysis; NMR; Plasma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolomics in noninvasive breast cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:3-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669185 Review.
-
Health-related quality of life in early breast cancer.Dan Med Bull. 2010 Sep;57(9):B4184. Dan Med Bull. 2010. PMID: 20816024
-
Metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of colorectal cancer.Cancer Lett. 2014 Apr 1;345(1):17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.011. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24333717 Review.
-
A role for biomarkers in the screening and diagnosis of breast cancer in younger women.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007 Sep;7(5):533-44. doi: 10.1586/14737159.7.5.533. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007. PMID: 17892362 Review.
-
["Screening" in special situations. Assessing predictive genetic screening for hereditary breast and colorectal cancer].Z Arztl Fortbild Qualitatssich. 2003 Feb;97(1):67-71. Z Arztl Fortbild Qualitatssich. 2003. PMID: 12669692 German.
Cited by
-
Can We Trust Score Plots?Metabolites. 2020 Jul 8;10(7):278. doi: 10.3390/metabo10070278. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32650451 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic analysis of human cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis diseases.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2016 Summer;9(3):158-73. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2016. PMID: 27458508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Cancer Metabolism: Applications of Metabolomics and Metabolic Phenotyping in Cancer Research and Diagnostics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:367-385. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34025-4_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32130709 Review.
-
Precision Oncology via NMR-Based Metabolomics: A Review on Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4687. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094687. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical models of amino acid panel for assisting diagnosis of children acute leukemia.J Transl Med. 2019 Jan 23;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1783-9. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30674317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen CM, Bro R. Variable selection in regression—a tutorial. Journal of Chemometrics. 2010;24:728–737. doi: 10.1002/cem.1360. - DOI
-
- Bellman R. Dynamic programming. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1957.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources