Autoimmunogenicity during anti-TNF therapy in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 26366147
- PMCID: PMC4565839
- DOI: 10.5114/pdia.2015.53320
Autoimmunogenicity during anti-TNF therapy in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: The tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) was initially described as lymphotoxin or cachectin. The discovery of therapies blocking the action of TNF-α, in 1988, started a new era in the therapy. One of often reported adverse effects related to the use of TNF-α antagonists is induction of the formation of autologous antibodies and antibodies neutralizing anti-TNF drugs. The development of anti-TNF-induced lupus or classical drug-induced lupus is more rarely reported.
Aim: To evaluate the presence and the level of anti-nuclear antibodies in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and the influence of anti-TNF therapy used on the concentration of antinuclear antibody (ANA).
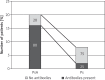
Material and methods: A total of 28 subjects were included in the study. 71.4% of subjects were diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis and 28.6% with plaque psoriasis.
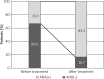
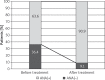
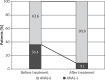
Results: Among the patients with plaque psoriasis, the antinuclear antibodies were found in 25% of subjects and in 80% of patients with psoriatic arthritis. After the treatment an increase in the titer or appearance of antibodies was found in 66.7% in the infliximab group, 18.2% in the etanercept group and 54.7% in the adalimumab group. No subjects developed symptoms of drug-induced systemic lupus.
Conclusions: Our findings have shown that all anti-TNF therapies induced ANA in psoriatic arthritis and psoriatic patients. Considering a mild course of lupus induced by anti-TNF treatment and, usually intrinsic, resolution of symptoms, the biological therapy still appears as a safe treatment for patients.
Keywords: anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy; anti-tumor necrosis factor-induced lupus; drug-induced lupus; psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Lubecka-Macura A, Kohut M. TNF superfamily – mechanisms of action, biological functions and therapeutic possibilities. Prz Gastroenterol. 2010;5:303–9.
-
- Szepietowski J, Adamski Z, Chodorowska G, et al. Guidelines of Polish Dermatological Society on the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris and arthropathic psoriasis (psoriatic arthritis) with biological drugs. Przegl Dermatol. 2010;97:1–13.
-
- Kolarz B, Targońska-Stępniak B, Darmochwał-Kolarz D, Majdan M. Autoimmune aspects of treatment with TNF-a inhibitors. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 2007;61:478–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
