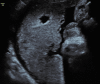
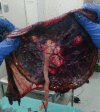
Placental damages in preeclampsia - from ultrasound images to histopathological findings
- PMID: 26366223
- PMCID: PMC4564041
Placental damages in preeclampsia - from ultrasound images to histopathological findings
Abstract
Preeclampsia is a unique pregnancy-related disease that affects 5-7% pregnancies worldwide. Placental architecture is modified in PE and eclampsia. Placental morphology and cellular arrangement are important for oxygen delivery from the mother to the fetus. Fetal growth and well-being after 20 weeks of gestation are dependent upon successful placental development. This, in turn, is achieved by an enhanced maternal blood supply to the placenta (normal uterine artery Doppler) and growth/ differentiation of the gas-exchanging placental villi. Conversely, pregnancy with severe placental insufficiency exhibits abnormalities both in uterine artery and in umbilical artery Doppler, and results in adverse perinatal outcome. The evaluation of placental functioning is possible nowadays through ultrasound examinations. Sonographic images associated with placental lesions include cystic areas, heterogeneous appearance of the placental mass, and thick or thin placentas. Sonographic evidence of destructive placental lesions is defined as the evolution of irregular cystic spaces with echogenic borders - the echogenic cystic lesions. Histological examinations of placenta may confirm these antepartum observations. Decidual vasculopathy and accelerated villous maturity are considered indicative of uteroplacental vascular insufficiency. Perivillous fibrin deposition and intervillous fibrin are considered indicative of intervillous coagulation. Detailed sonographic evaluation of the placenta and histopathological confirmation after birth are used to identify lesions associated with preeclampsia, intrauterine growth restriction and adverse short and long-term perinatal outcome, but the presence of cystic images in the placenta is not uniformly associated with adverse perinatal outcome. Combining Doppler studies with placental texture studies may lead to satisfactory results.
Keywords: cystic areas; echogenic cystic lesion; intraplacental haematomas; placenta; preeclampsia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic utility of serial circulating placental growth factor levels and uterine artery Doppler waveforms in diagnosing underlying placental diseases in pregnancies at high risk of placental dysfunction.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Oct;227(4):618.e1-618.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.05.043. Epub 2022 May 27. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 35644246
-
The association between decidual vasculopathy and abnormal uterine artery Doppler measurement.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022 Aug;101(8):910-916. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14345. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022. PMID: 35684972 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of placental-derived fetal growth restriction.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Feb;218(2S):S745-S761. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.11.577. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29422210 Review.
-
Prognostic value of placental ultrasound in pregnancies complicated by absent end-diastolic flow velocity in the umbilical arteries.Placenta. 2004 Sep-Oct;25(8-9):735-41. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2004.03.002. Placenta. 2004. PMID: 15450392
-
A placenta clinic approach to the diagnosis and management of fetal growth restriction.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Feb;218(2S):S803-S817. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.11.575. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29254754 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress and Placental Pathogenesis: A Contemporary Overview of Potential Biomarkers and Emerging Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 13;25(22):12195. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212195. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology and placental pathology of intrauterine fetal demise in a tertiary hospital in the Philippines.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2024 Aug 27;23:100338. doi: 10.1016/j.eurox.2024.100338. eCollection 2024 Sep. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2024. PMID: 39286338 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol for a prospective cohort study to investigate Hemodynamic Adaptation to Pregnancy and Placenta-related Outcome: the HAPPO study.BMJ Open. 2019 Nov 10;9(11):e033083. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033083. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31712350 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological study of annexin A5 & apelin in pre-eclamptic placentae with emphasis on foetal outcome.Indian J Med Res. 2021 Jun;154(6):813-822. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_433_21. Indian J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 35662086 Free PMC article.
-
The Pivotal Role of the Placenta in Normal and Pathological Pregnancies: A Focus on Preeclampsia, Fetal Growth Restriction, and Maternal Chronic Venous Disease.Cells. 2022 Feb 6;11(3):568. doi: 10.3390/cells11030568. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alkazaleh F, Viero S, Simchen M. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2004 May;23, 5:472–476. - PubMed
-
- Burton GJ, Jauniaux E, Charnock-Jones DS. The influence of the intrauterine environment on human placental development. Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Dekan S, Linduska N, Kasprian G, Prayer D. MRI of the placenta - a short review. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2012;162:225–228. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald B, Shannon P, Kingdom J, Keating S. Rounded intraplacental haematomas due to decidual vasculopathy have a distinctive morphology. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64:729–732. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources