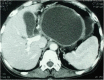
Valproic Acid-Induced Severe Acute Pancreatitis with Pseudocyst Formation: Report of a Case
- PMID: 26366333
- PMCID: PMC4564375
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.297
Valproic Acid-Induced Severe Acute Pancreatitis with Pseudocyst Formation: Report of a Case
Abstract
Valproic acid is the most widely used anti-epilep-tic drug in children, and it is probably the most frequent cause of drug-induced acute pancreatitis. Outcomes for patients with valproic acid-associated pancreatitis vary from full recovery after discontinuation of the drug to severe acute pancreatitis and death. Here, we present a case of valproic acid-induced severe acute pancreatitis with pseudocyst formation in a 10-year-old girl with cerebral palsy and generalized tonic-clonic seizure. There was no resolution of the pseudocyst after discontinuation of valproic acid. The patient became symptomatic with a progressive increase in the size of the pseudocyst. She was successfully treated with cystogastrostomy and was well at 12-month follow-up.
Keywords: cystogastrostomy; pancreatitis; pseudocyst; valproic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Pancreatitis associated with valproic acid: a review of the literature. Chapman SA, Wacksman GP, Patterson BD. Pharmacotherapy. 2001;21:1549–1560. - PubMed
-
- Idiosyncratic adverse reactions to antiepileptic drugs. Zaccara G, Franciotta D, Perucca E. Epilepsia. 2007;48:1223–1244. - PubMed
-
- Valproic acid-induced pancreatitis: 16 new cases and a review of the literature. Gerstner T, Büsing D, Bell N, Longin E, Kasper JM, Klostermann W, Hebing B, Hanefeld F, Eckel U, Hoffmann R, Bettendorf U, Weidner B, Wiemer-Kruel A, Brockmann K, Neumann FW, Sandrieser T, Wolff M, König S. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Pancreatitis associated with valproic acid therapy. Batalden PB, Van Dyne BJ, Cloyd J. Pediatrics. 1979;64:520–522. - PubMed
-
- Pancreatitis due to valproic acid. Camfield PR, Bagnell P, Camfield CS, Tibbles JA. Lancet. 1979;1:1198–1199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources