Lung abscess-etiology, diagnostic and treatment options
- PMID: 26366400
- PMCID: PMC4543327
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.07.08
Lung abscess-etiology, diagnostic and treatment options
Abstract
Lung abscess is a type of liquefactive necrosis of the lung tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm) containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection. It can be caused by aspiration, which may occur during altered consciousness and it usually causes a pus-filled cavity. Moreover, alcoholism is the most common condition predisposing to lung abscesses. Lung abscess is considered primary (60%) when it results from existing lung parenchymal process and is termed secondary when it complicates another process, e.g., vascular emboli or follows rupture of extrapulmonary abscess into lung. There are several imaging techniques which can identify the material inside the thorax such as computerized tomography (CT) scan of the thorax and ultrasound of the thorax. Broad spectrum antibiotic to cover mixed flora is the mainstay of treatment. Pulmonary physiotherapy and postural drainage are also important. Surgical procedures are required in selective patients for drainage or pulmonary resection. In the current review we will present all current information from diagnosis to treatment.
Keywords: Lung abscess; antibiotics; thoracoscopy; video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
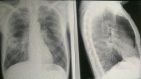

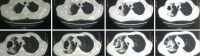



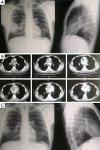


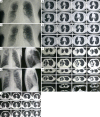
References
-
- Seo H, Cha SI, Shin KM, et al. Focal necrotizing pneumonia is a distinct entity from lung abscess. Respirology 2013;18:1095-100. - PubMed
-
- Yazbeck MF, Dahdel M, Kalra A, et al. Lung abscess: update on microbiology and management. Am J Ther 2014;21:217-21. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JG. The role of anaerobic bacteria in lung abscess. Clin Infect Dis 2005;40:923-5. - PubMed
-
- Schweigert M, Dubecz A, Stadlhuber RJ, et al. Modern history of surgical management of lung abscess: from Harold Neuhof to current concepts. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;92:2293-7. - PubMed
-
- Moreira Jda S, Camargo Jde J, Felicetti JC, et al. Lung abscess: analysis of 252 consecutive cases diagnosed between 1968 and 2004. J Bras Pneumol 2006;32:136-43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
