Current status and future prospects of yellow fever vaccines
- PMID: 26366673
- PMCID: PMC5563254
- DOI: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1083430
Current status and future prospects of yellow fever vaccines
Abstract
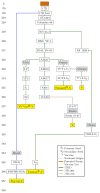
Yellow fever 17D vaccine is one of the oldest live-attenuated vaccines in current use that is recognized historically for its immunogenic and safe properties. These unique properties of 17D are presently exploited in rationally designed recombinant vaccines targeting not only flaviviral antigens but also other pathogens of public health concern. Several candidate vaccines based on 17D have advanced to human trials, and a chimeric recombinant Japanese encephalitis vaccine utilizing the 17D backbone has been licensed. The mechanism(s) of attenuation for 17D are poorly understood; however, recent insights from large in silico studies have indicated particular host genetic determinants contributing to the immune response to the vaccine, which presumably influences the considerable durability of protection, now in many cases considered to be lifelong. The very rare occurrence of severe adverse events for 17D is discussed, including a recent fatal case of vaccine-associated viscerotropic disease.
Keywords: empiric; empiric vaccine; flavivirus; live-attenuated; primary seed; rational vaccine; recombinant vaccine; secondary seed; vaccine; viral diversity; yellow fever virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors were supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R21 AI 113407) and the Gillson-Longenbaugh Foundation. AS Beck was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grant T32 AI 060549. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures
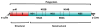
References
-
- Vainio J, Cutts F. Yellow Fever. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1998.
-
- Bazin H. Yellow Fever Vaccine. Vaccinations: A History: John Libbey Eurotext. 2011:407–54.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO-recommended standards for surveillance of selected vaccine preventable diseases. 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
