The Internal Dynamics of Fibrinogen and Its Implications for Coagulation and Adsorption
- PMID: 26366880
- PMCID: PMC4569070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004346
The Internal Dynamics of Fibrinogen and Its Implications for Coagulation and Adsorption
Abstract
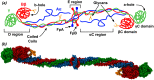
Fibrinogen is a serum multi-chain protein which, when activated, aggregates to form fibrin, one of the main components of a blood clot. Fibrinolysis controls blood clot dissolution through the action of the enzyme plasmin, which cleaves fibrin at specific locations. Although the main biochemical factors involved in fibrin formation and lysis have been identified, a clear mechanistic picture of how these processes take place is not available yet. This picture would be instrumental, for example, for the design of improved thrombolytic or anti-haemorrhagic strategies, as well as, materials with improved biocompatibility. Here, we present extensive molecular dynamics simulations of fibrinogen which reveal large bending motions centered at a hinge point in the coiled-coil regions of the molecule. This feature, likely conserved across vertebrates according to our analysis, suggests an explanation for the mechanism of exposure to lysis of the plasmin cleavage sites on fibrinogen coiled-coil region. It also explains the conformational variability of fibrinogen observed during its adsorption on inorganic surfaces and it is supposed to play a major role in the determination of the hydrodynamic properties of fibrinogen. In addition the simulations suggest how the dynamics of the D region of fibrinogen may contribute to the allosteric regulation of the blood coagulation cascade through a dynamic coupling between the a- and b-holes, important for fibrin polymerization, and the integrin binding site P1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties.Subcell Biochem. 2017;82:405-456. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49674-0_13. Subcell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28101869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of fibrinogen D domain intermolecular association sites in the polymerization of fibrin and fibrinogen Tokyo II (gamma 275 Arg-->Cys).J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):1053-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI118091. J Clin Invest. 1995. PMID: 7635941 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of fibrin clot elasticity.Structure. 2008 Mar;16(3):449-59. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.12.019. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Structure. 2008. PMID: 18294856
-
Molecular Dynamics of Fibrinogen Adsorption onto Graphene, but Not onto Poly(ethylene glycol) Surface, Increases Exposure of Recognition Sites That Trigger Immune Response.J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Apr 25;56(4):706-20. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00703. Epub 2016 Mar 23. J Chem Inf Model. 2016. PMID: 26966807
-
Fibrinogen and factor XIII at the intersection of coagulation, fibrinolysis and inflammation.Thromb Haemost. 2014 Oct;112(4):649-58. doi: 10.1160/TH14-01-0085. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25182841 Review.
Cited by
-
vhp Is a Fibrinogen-Binding Protein Related to vWbp in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0116721. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01167-21. Epub 2021 Aug 3. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34340548 Free PMC article.
-
The absence of thrombin-like activity in Bothrops erythromelas venom is due to the deletion of the snake venom thrombin-like enzyme gene.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 27;16(4):e0248901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248901. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33905416 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of Interfacial Flexibility in Fibrin Oligomers.Structure. 2016 Nov 1;24(11):1907-1917. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27692965 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinogen and Fibrin.Subcell Biochem. 2021;96:471-501. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58971-4_15. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33252741 Review.
-
Adsorption of Fibrinogen on Silica Surfaces-The Effect of Attached Nanoparticles.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 6;10(3):413. doi: 10.3390/biom10030413. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32155964 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

