Toll-like receptor 4 signaling: A common pathway for interactions between prooxidants and extracellular disulfide high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein-coupled activation
- PMID: 26367307
- PMCID: PMC4600681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.08.109
Toll-like receptor 4 signaling: A common pathway for interactions between prooxidants and extracellular disulfide high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein-coupled activation
Abstract
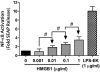
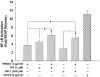
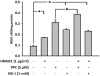
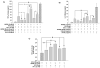
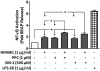
Necrotic cells passively release HMGB1, which can stimulate TLR4 in an autocrine fashion to potentially initiate "sterile" inflammation that maintains different disease states. We have shown that prooxidants can induce NF-κB activation through TLR4 stimulation. We examined whether prooxidants enhance HMGB1-induced TLR4 signaling through NF-κB activation. We used LPS-EK as a specific agonist for TLR4, and PPC and SIN-1 as in situ sources for ROS. As model systems, we used HEK-Blue cells (stably transfected with mouse TLR4), RAW-Blue™ cells (derived from murine RAW 264.7 macrophages) and primary murine macrophages from TLR4-KO mice. Both HEK-Blue and RAW-Blue 264.7 cells express optimized secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter under the control of a promoter inducible by NF-κB. We treated cells with HMGB1 alone and/or in conjunction with prooxidants and/or inhibitors using SEAP release as a measure of TLR4 stimulation. HMGB1 alone and/or in conjunction with prooxidants increased TNFα and IL-6 released from TLR4-WT, but not from TLR4-KO macrophages. Pro-oxidants increased HMGB1 release, which we quantified by ELISA. We used both fluorescence microscopy imaging and flow cytometry to quantify the expression of intracellular ROS. TLR4-neutralizing antibody decreased prooxidant-induced HMGB1 release. Prooxidants promoted HMGB1-induced NF-κB activation as determined by increased release of SEAP and TNF-α, and accumulation of iROS. HMGB1 (Box A), anti-HMGB1 and anti-TLR4-neutralizing pAbs inhibited HMGB1-induced NF-κB activation, but HMGB1 (Box A) and anti-HMGB1 pAb had no effect on prooxidant-induced SEAP release. The present results confirm that prooxidants enhance proinflammatory effects of HMGB1 by activating NF-κB through TLR4 signaling.
Keywords: NF-κB activation; Prooxidants; Recombinant high mobility group box 1 protein; Sterile inflammation; Toll-like receptor 4.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Davies KJ. Oxidative stress: the paradox of aerobic life. Biochem Soc Symp. 1995;61:1–31. - PubMed
-
- Giustarini D, Dalle-Donne I, Tsikas D, Rossi R. Oxidative stress and human diseases: Origin, link, measurement, mechanisms, and biomarkers. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2009;46(5-6):241–281. - PubMed
-
- Davies KJ. Oxidative stress, antioxidant defenses, and damage removal, repair, and replacement systems. IUBMB Life. 2000;50(4-5):279–289. Review. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

